Unfolding SARS-CoV-2 viral genome to understand its gene expression regulation
- PMID: 32473977
- PMCID: PMC7256514
- DOI: 10.1016/j.meegid.2020.104386
Unfolding SARS-CoV-2 viral genome to understand its gene expression regulation
Abstract
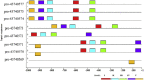
SARS-CoV-2 is a new virus responsible for an outbreak of respiratory illness known as COVID-19, which has spread to several countries around the world and a global effort is being undertaken to characterize the molecular features and evolutionary origins of this virus. In silico analysis of the transcription start sites, promoter regions, transcription factors and their binding sites, gene ontology, CpG islands for SARS-CoV-2 viral genome are a first step to understand the regulation mechanisms of gene expression and its association with genetic variations in the genomes. For this purpose, we first computationally surveyed all SARS-CoV-2 virus genes with the open reading frames from NCBI database and found eleven sequences to accomplish the mentioned features by using bioinformatics tools. Our analysis revealed that all (100%) of the SARS-CoV-2 virus genes have more than one TSS. By taking all TSSs with the highest predictive score we determined promoter regions and identified five common candidate motifs (MVI, MVII, MVIII, MVIV and MVV) of which MVI was found to be shared by all promoter regions of SARS-CoV-2 virus genes with the least E-value (3.8e-056, statistically highly significant). In our further analysis of MVI we showed MVI serve as binding sites for a single transcription factor (TF) family, EXPREG, involved in the regulatory mode of these genes. From EXPREG family four TFs that belongs to Cyclic AMP (cAMP) receptor protein (CRP) and Catabolite control protein A (CcpA) group mostly serve as transcriptional activator whereas two TFs that belong to LexA group always serve as transcriptional repressor in different kinds of cellular processes and molecular functions. Therefore, we unfolded SARS-CoV-2 viral genome to shed light on its gene expression regulation that could help to design and evaluate diagnostic tests, to track and trace the ongoing outbreak and to identify potential intervention options.
Keywords: COVID-19; CpG Island; Motif; Promoter; SARS-CoV-2; Transcription factor.
Copyright © 2020 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures
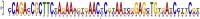
References
-
- Bailey L.T., Elkan C. Proceedings of the Second International Conference on Intelligent Systems for MolecularBiology. AAAI Press; 1994. Fitting a mixture model by expectation maximization to discover motifs in biopolymers; pp. 28–36. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

