Human Liver Microsomes Immobilized on Magnetizable Beads: A Novel Approach to Study In Vitro Drug Metabolism
- PMID: 32474441
- PMCID: PMC7370995
- DOI: 10.1124/dmd.120.090696
Human Liver Microsomes Immobilized on Magnetizable Beads: A Novel Approach to Study In Vitro Drug Metabolism
Abstract
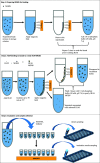
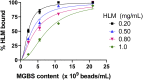
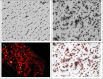
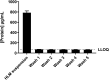
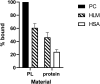
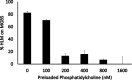
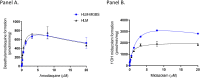
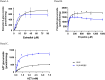
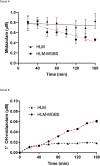
Human liver microsomes (HLM) are a commonly used tool to study drug metabolism in vitro. Typical experiments conducted using suspensions of HLM can be challenging to separate from the incubation solution without lengthy ultracentrifugation steps. Magnetizable beads coated with silica (MGBS) were found to bind strongly to HLM, which could then be isolated and purified using a magnet. Binding of HLM to the MGBS (HLM-MGBS) was demonstrated to be mediated by strong interactions between microsomal phospholipids and MGBS, as artificially prepared phosphatidylcholine (PC) liposomes could be more efficiently captured by the MGBS. HLM-MGBS complexes retained functional cytochrome P450 and uridine-diphosphate-glucuronosyltransferase (UGT) activity as indicated by CYP2C8-mediated amodiaquine de-ethylation, CYP3A4-mediated midazolam 1'hydroxylation, UGT1A1-mediated glucuronidation of estradiol, UGT1A9-mediated glucuronidation of propofol, and UGT2B7-mediated glucuronidation of zidovudine. When comparing suspension HLM alone with HLM-MGBS complexes containing equivalent amounts of HLM, the intrinsic clearance (CLint) of CYP450 substrates was comparable; however, CLint of UGT1A1, UGT1A9, and UGT2B7 was increased in the HLM-MGBS system between 1.5- and 6-fold. HLM-MGBS used in an incubation could also be readily replaced with fresh HLM-MGBS to maintain the presence of active enzymes. Thus, HLM-MGBS demonstrate increased in vitro metabolic efficiency and manipulability, providing a new platform for determination of accurate metabolic parameters. SIGNIFICANCE STATEMENT: The following work describes the strong binding of HLM to magnetizable beads. In addition, the preservation of enzyme activity on the bound HLM provides a novel means to conduct preclinical metabolism studies.
Copyright © 2020 by The American Society for Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics.
Figures
References
-
- Achour B, Al Feteisi H, Lanucara F, Rostami-Hodjegan A, Barber J. (2017) Global proteomic analysis of human liver microsomes: rapid characterization and quantification of hepatic drug-metabolizing enzymes. Drug Metab Dispos 45:666–675. - PubMed
-
- Berka K, Paloncýová M, Anzenbacher P, Otyepka M. (2013) Behavior of human cytochromes P450 on lipid membranes. J Phys Chem B 117:11556–11564. - PubMed
-
- Bradford MM. (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

