Profiling serum cytokines in COVID-19 patients reveals IL-6 and IL-10 are disease severity predictors
- PMID: 32475230
- PMCID: PMC7473317
- DOI: 10.1080/22221751.2020.1770129
Profiling serum cytokines in COVID-19 patients reveals IL-6 and IL-10 are disease severity predictors
Abstract
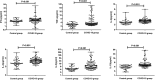
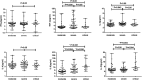
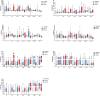
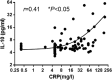
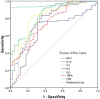
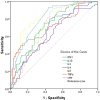
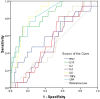
Since the outbreak of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) in Wuhan, China, it has rapidly spread across many other countries. While the majority of patients were considered mild, critically ill patients involving respiratory failure and multiple organ dysfunction syndrome are not uncommon, which could result death. We hypothesized that cytokine storm is associated with severe outcome. We enrolled 102 COVID-19 patients who were admitted to Renmin Hospital (Wuhan, China). All patients were classified into moderate, severe and critical groups according to their symptoms. 45 control samples of healthy volunteers were also included. Inflammatory cytokines and C-Reactive Protein (CRP) profiles of serum samples were analyzed by specific immunoassays. Results showed that COVID-19 patients have higher serum level of cytokines (TNF-α, IFN-γ, IL-2, IL-4, IL-6 and IL-10) and CRP than control individuals. Within COVID-19 patients, serum IL-6 and IL-10 levels are significantly higher in critical group (n = 17) than in moderate (n = 42) and severe (n = 43) group. The levels of IL-10 is positively correlated with CRP amount (r = 0.41, P < 0.01). Using univariate logistic regression analysis, IL-6 and IL-10 are found to be predictive of disease severity and receiver operating curve analysis could further confirm this result (AUC = 0.841, 0.822 respectively). Our result indicated higher levels of cytokine storm is associated with more severe disease development. Among them, IL-6 and IL-10 can be used as predictors for fast diagnosis of patients with higher risk of disease deterioration. Given the high levels of cytokines induced by SARS-CoV-2, treatment to reduce inflammation-related lung damage is critical.
Keywords: COVID-19; Interleukin 10; Interleukin 6; SARS-CoV-2; cytokine storm; inflammatory cytokines.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
