IgG4-related Autoimmune Hepatitis with a Suspected Drug-induced Etiology
- PMID: 32475907
- PMCID: PMC7332635
- DOI: 10.2169/internalmedicine.4092-19
IgG4-related Autoimmune Hepatitis with a Suspected Drug-induced Etiology
Abstract
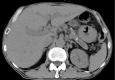
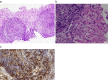
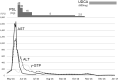
A 69-year-old man was referred to our department with acute hepatitis. He had been newly treated with benidipine hydrochloride for two months. His blood test results were as follows: aspartate aminotransferase, 1,614 IU/L; alanine aminotransferase, 1,091 IU/L and anti-smooth muscle antibody, ×80. Needle liver biopsy specimen showed interface hepatitis with mainly lymphocytic infiltration and bridging fibrosis in the periportal area. Immunohistochemistry revealed lymphocytic infiltration positive for IgG4. We diagnosed him with IgG4-related AIH with an etiology that was suspected of being drug-induced. Oral prednisolone was started and then tapered after achieving biochemical remission. Hepatitis recurred after the cessation of steroids; however, remission was achieved with ursodeoxycholic acid.
Keywords: IgG4; autoimmune hepatitis; drug-induced.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Recent progress in the diagnosis and therapy of autoimmune hepatitis].Nihon Naika Gakkai Zasshi. 1999 Sep 10;88(9):1763-7. Nihon Naika Gakkai Zasshi. 1999. PMID: 10581761 Review. Japanese. No abstract available.
-
Acute seronegative autoimmune hepatitis.Hepatogastroenterology. 2010 Mar-Apr;57(98):334-5. Hepatogastroenterology. 2010. PMID: 20583438
-
A case of primary biliary cholangitis overlapping with type 2 autoimmune hepatitis.Clin J Gastroenterol. 2020 Feb;13(1):79-82. doi: 10.1007/s12328-019-01017-2. Epub 2019 Jul 8. Clin J Gastroenterol. 2020. PMID: 31286423
-
Clinical and biochemical features and therapy responses in primary biliary cirrhosis and primary biliary cirrhosis-autoimmune hepatitis overlap syndrome.Hepatogastroenterology. 2002 Sep-Oct;49(47):1195-200. Hepatogastroenterology. 2002. PMID: 12239904
-
Autoimmune hepatitis in human immunodeficiency virus-infected patients: A case series and review of the literature.World J Gastroenterol. 2019 Sep 21;25(35):5388-5402. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i35.5388. World J Gastroenterol. 2019. PMID: 31558881 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A case of immunoglobulin G4-related kidney disease manifesting after dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor treatment.CEN Case Rep. 2024 Dec;13(6):565-572. doi: 10.1007/s13730-024-00889-9. Epub 2024 May 27. CEN Case Rep. 2024. PMID: 38801515 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Björnsson E. Review article: drug-induced liver injury in clinical practice. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 32: 3-13, 2010. - PubMed
-
- Björnsson E, Talwalkar J, Treeprasertsuk S, et al. . Drug-induced autoimmune hepatitis: clinical characteristics and prognosis. Hepatology 51: 2040-2048, 2010. - PubMed
-
- Weiler-Normann C, Schramm C. Drug induced liver injury and its relationship to autoimmune hepatitis. J Hepatol 55: 747-749, 2011. - PubMed

