Observer-Based Deconvolution of Deterministic Input in Coprime Multichannel Systems With Its Application to Noninvasive Central Blood Pressure Monitoring
- PMID: 32476675
- PMCID: PMC7247534
- DOI: 10.1115/1.4047060
Observer-Based Deconvolution of Deterministic Input in Coprime Multichannel Systems With Its Application to Noninvasive Central Blood Pressure Monitoring
Abstract
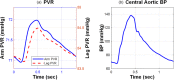
Estimating central aortic blood pressure (BP) is important for cardiovascular (CV) health and risk prediction purposes. CV system is a multichannel dynamical system that yields multiple BPs at various body sites in response to central aortic BP. This paper concerns the development and analysis of an observer-based approach to deconvolution of unknown input in a class of coprime multichannel systems applicable to noninvasive estimation of central aortic BP. A multichannel system yields multiple outputs in response to a common input. Hence, the relationship between any pair of two outputs constitutes a hypothetical input-output system with unknown input embedded as a state. The central idea underlying our approach is to derive the unknown input by designing an observer for the hypothetical input-output system. In this paper, we developed an unknown input observer (UIO) for input deconvolution in coprime multichannel systems. We provided a universal design algorithm as well as meaningful physical insights and inherent performance limitations associated with the algorithm. The validity and potential of our approach were illustrated using a case study of estimating central aortic BP waveform from two noninvasively acquired peripheral arterial pulse waveforms. The UIO could reduce the root-mean-squared error (RMSE) associated with the central aortic BP by up to 27.5% and 28.8% against conventional inverse filtering (IF) and peripheral arterial pulse scaling techniques.
Copyright © 2020 by ASME.
Figures
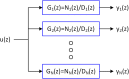
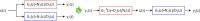
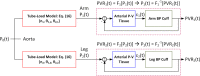
![Observer-based deconvolution of central aortic BP waveform from noninvasive peripheral arterial pulse waveform measurements. The PVRs are made at the upper arm and leg sites using the BP cuffs loaded at a subdiastolic pressure level. These diametric PVR signals are applied to a system identification procedure [20] to derive the channel dynamics associated with (i) the propagation of the BP wave from the aorta to the peripheral arteries and (ii) the propagation and distortion of the peripheral BP waves into the PVR signals at the respective peripheral measurement sites. The UIO designed using the estimated channel dynamics estimates central aortic BP from peripheral PVR signals.](https://cdn.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/blobs/45e4/7247534/ddb7d10d0a11/ds-19-1309_091006_g003.gif)
Similar articles
-
Blind identification of the aortic pressure waveform from multiple peripheral artery pressure waveforms.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2007 May;292(5):H2257-64. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.01159.2006. Epub 2007 Jan 5. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2007. PMID: 17208992
-
Application of the N-point moving average method for brachial pressure waveform-derived estimation of central aortic systolic pressure.Hypertension. 2014 Apr;63(4):865-70. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.113.02229. Epub 2014 Jan 13. Hypertension. 2014. PMID: 24420554
-
Measurement of central aortic pulse pressure: noninvasive brachial cuff-based estimation by a transfer function vs. a novel pulse wave analysis method.Am J Hypertens. 2012 Nov;25(11):1162-9. doi: 10.1038/ajh.2012.116. Epub 2012 Aug 9. Am J Hypertens. 2012. PMID: 22874891
-
Improved pulse transit time estimation by system identification analysis of proximal and distal arterial waveforms.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2011 Oct;301(4):H1389-95. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00443.2011. Epub 2011 Jul 29. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2011. PMID: 21803948
-
Clinical measurement of arterial stiffness obtained from noninvasive pressure waveforms.Am J Hypertens. 2005 Jan;18(1 Pt 2):3S-10S. doi: 10.1016/j.amjhyper.2004.10.009. Am J Hypertens. 2005. PMID: 15683725 Review.
References
-
- Benjamin, E. J. , Virani, S. S. , Callaway, C. W. , Chamberlain, A. M. , Chang, A. R. , Cheng, S. , Chiuve, S. E. , Cushman, M. , Delling, F. N. , Deo, R. , De Ferranti, S. D. , Ferguson, J. F. , Fornage, M. , Gillespie, C. , Isasi, C. R. , Jiménez, M. C. , Jordan, L. C. , Judd, S. E. , Lackland, D. , Lichtman, J. H. , Lisabeth, L. , Liu, S. , Longenecker, C. T. , Lutsey, P. L. , MacKey, J. S. , Matchar, D. B. , Matsushita, K. , Mussolino, M. E. , Nasir, K. , O'Flaherty, M. , Palaniappan, L. P. , Pandey, A. , Pandey, D. K. , Reeves, M. J. , Ritchey, M. D. , Rodriguez, C. J. , Roth, G. A. , Rosamond, W. D. , Sampson, U. K. A. , Satou, G. M. , Shah, S. H. , Spartano, N. L. , Tirschwell, D. L. , Tsao, C. W. , Voeks, J. H. , Willey, J. Z. , Wilkins, J. T. , Wu, J. H. Y. , Alger, H. M. , Wong, S. S. , and Muntner, P. , 2018, “ Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics—2018 Update: A Report From the American Heart Association,” Circulation, 137(12), pp. e67–e492.10.1161/CIR.0000000000000558 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ferguson, J. M. , Minas, J. , Siapantas, S. , Komesaroff, P. A. , and Sudhir, K. , 2008, “ Effects of a Fixed-Dose ACE Inhibitor-Diuretic Combination on Ambulatory Blood Pressure and Arterial Properties in Isolated Systolic Hypertension,” J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol., 51(6), pp. 590–595.10.1097/FJC.0b013e31817a8316 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Roman, M. J. , Okin, P. M. , Kizer, J. R. , Lee, E. T. , Howard, B. V. , and Devereux, R. B. , 2010, “ Relations of Central and Brachial Blood Pressure to Left Ventricular Hypertrophy and Geometry: The Strong Heart Study,” J. Hypertens., 28(2), pp. 384–388.10.1097/HJH.0b013e328333d228 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Roman, M. J. , Devereux, R. B. , Kizer, J. R. , Lee, E. T. , Galloway, J. M. , Ali, T. , Umans, J. G. , and Howard, B. V. , 2007, “ Central Pressure More Strongly Relates to Vascular Disease and Outcome Than Does Brachial Pressure: The Strong Heart Study,” Hypertension, 50(1), pp. 197–203.10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.107.089078 - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
