New role for ceramide in hypoxia and insulin resistance
- PMID: 32476784
- PMCID: PMC7235208
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i18.2177
New role for ceramide in hypoxia and insulin resistance
Abstract
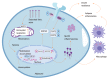
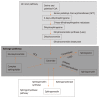
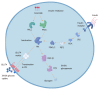
Ceramides are significant metabolic products of sphingolipids in lipid metabolism and are associated with insulin resistance and hepatic steatosis. In chronic inflammatory pathological conditions, hypoxia occurs, the metabolism of ceramide changes, and insulin resistance arises. Hypoxia-inducible factors (HIFs) are a family of transcription factors activated by hypoxia. In hypoxic adipocytes, HIF-1α upregulates pla2g16 (a novel HIF-1α target gene) gene expression to activate the NLRP3 inflammasome pathway and stimulate insulin resistance, and adipocyte-specific Hif1a knockout can ameliorate homocysteine-induced insulin resistance in mice. The study on the HIF-2α-NEU3-ceramide pathway also reveals the role of ceramide in hypoxia and insulin resistance in obese mice. Under obesity-induced intestinal hypoxia, HIF-2α increases the production of ceramide by promoting the expression of the gene Neu3 encoding sialidase 3, which is a key enzyme in ceramide synthesis, resulting in insulin resistance in high-fat diet-induced obese mice. Moreover, genetic and pathophysiologic inhibition of the HIF-2α-NEU3-ceramide pathway can alleviate insulin resistance, suggesting that these could be potential drug targets for the treatment of metabolic diseases. Herein, the effects of hypoxia and ceramide, especially in the intestine, on metabolic diseases are summarized.
Keywords: Ceramide; Diabetes mellitus; Hypoxia-inducible factors; Insulin resistance; Intestinal hypoxia; Obesity.
©The Author(s) 2020. Published by Baishideng Publishing Group Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: There is no conflict of interest associated with any of the senior author or other coauthors who contributed their efforts in this manuscript.
Figures
References
-
- Federation ID. IDF Diabetes Atlas, 9th edition 2019. Brussels, Belgium. Available from: https://www.diabetesatlas.org/en/sections/proven-and-effective-actions.html.
-
- Shoelson SE, Herrero L, Naaz A. Obesity, inflammation, and insulin resistance. Gastroenterology. 2007;132:2169–2180. - PubMed
-
- Dali-Youcef N, Mecili M, Ricci R, Andrès E. Metabolic inflammation: connecting obesity and insulin resistance. Ann Med. 2013;45:242–253. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

