Combined pirfenidone, azithromycin and prednisolone in post-H1N1 ARDS pulmonary fibrosis
- PMID: 32476885
- PMCID: PMC7170064
- DOI: 10.36141/svdld.v35i1.6393
Combined pirfenidone, azithromycin and prednisolone in post-H1N1 ARDS pulmonary fibrosis
Abstract
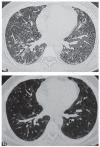
There are no specific data on the management of pulmonary fibrosis post-H1N1 ARDS. We present the cases of three patients who responded positively to treatment with pirfenidone, azithromycin and prednisolone. Three males, aged 40, 45 and 59 years, had H1N1 ARDS requiring mechanical ventilation for two weeks or longer. After weaning off ventilation, they had persistent symptoms and hypoxemia at rest despite receiving prednisolone and home oxygen for at least three weeks following discharge. Computed tomography (CT) of the chest showed fibrosis and traction bronchiectasis. At presentation, they could not perform spirometry. Investigations ruled out infection. Pirfenidone (600 mg daily escalated to maximum tolerable dose of 2.4 gm daily) and azithromycin (500 mg thrice weekly) were added off-label to prednisolone. In one patient pirfenidone was discontinued after three months due to an adverse reaction and azithromycin was continued for nine months. At one year follow-up, all patients had symptomatic improvement, better effort tolerance, regression of opacities and no progression of fibrosis on CT, and improvement in spirometry and six minute walk tests. Pirfenidone and azithromycin added to prednisolone may have led to clinical and radiological improvement. The current experience suggests that this treatment approach to pulmonary fibrosis post-H1N1 ARDS be studied further. (Sarcoidosis Vasc Diffuse Lung Dis 2018; 35: 85-90).
Keywords: ARDS; H1N1; azithromycin; pirfenidone; prednisolone; pulmonary fibrosis.
Copyright: © 2018.
Figures


References
-
- American Thoracic Society (ATS), European Respiratory Society (ERS) Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: diagnosis and treatment. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2000;161:646–64. - PubMed
-
- Biffl WL, Moore FA, Moore EE, Haenel JB, McIntyre RC, Jr, Burch JM. Are corticosteroids salvage therapy for refractory acute respiratory distress syndrome. Am J Surg. 1995;170:591–6. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
