Cathepsin S, a new serum biomarker of sarcoidosis discovered by transcriptome analysis of alveolar macrophages
- PMID: 32476947
- PMCID: PMC7247107
- DOI: 10.36141/svdld.v36i2.7620
Cathepsin S, a new serum biomarker of sarcoidosis discovered by transcriptome analysis of alveolar macrophages
Abstract
Background: Development of reliable new biomarkers remains crucial to improve diagnosis and assessing disease activity in sarcoidosis. The objective of this study was to seek such markers from the gene expression signature of alveolar macrophages by transcriptome analysis.
Methods: Pooled RNA extracted from alveolar macrophages from patients with active sarcoidosis and control patients was subjected to transcriptome analysis using microarrays. Expressed gene intensity in sarcoidosis relative to that in control was calculated. We measured serum cathepsin S (CTSS) concentrations in 89 healthy volunteers, 107 patients with sarcoidosis, 26 with interstitial pneumonia, 150 with pneumoconiosis, and 76 with pulmonary mycobacteriosis by the enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay.
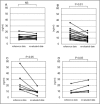
Results: Among 12 genes with ratios higher than that of a housekeeping gene, we selected CTSS for scrutinizing protein expression in serum because of the feasibility of the protein assay. CTSS concentrations were significantly increased in sarcoidosis compared with not only controls but also all the other lung diseases. Receiver operating characteristics curve for sarcoidosis and parenchymal lung diseases revealed an area under the curve of 0.800 (95% confidence interval, 0.751-0.850; p=1.4 x 10-18) with 70% sensitivity and 78% specificity at a CTSS concentration of 15.5 ng/ml. A significant trend was identified between CTSS concentrations and the number of affected organs. Serum CTSS concentrations varied in parallel with clinical courses both spontaneously and in response to corticosteroid therapy. Epithelioid cells in granulomas were positive for immunohistochemical staining with CTSS.
Conclusions: CTSS has the potential to be a useful biomarker in sarcoidosis.
Keywords: biomarkers; cathepsins; macrophages; sarcoidosis; transcriptome.
Copyright: © 2019.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Increased production of matrix metalloproteinase-2 in alveolar macrophages and regulation by interleukin-10 in patients with acute pulmonary sarcoidosis.Exp Lung Res. 2002 Jan-Feb;28(1):55-68. doi: 10.1080/019021402753355535. Exp Lung Res. 2002. PMID: 11792075
-
Preliminary characterizations of a serum biomarker for sarcoidosis by comparative proteomic approach with tandem-mass spectrometry in ethnic Han Chinese patients.Respir Res. 2013 Feb 11;14(1):18. doi: 10.1186/1465-9921-14-18. Respir Res. 2013. PMID: 23399022 Free PMC article.
-
Differential transcriptomics in sarcoidosis lung and lymph node granulomas with comparisons to pathogen-specific granulomas.Respir Res. 2020 Dec 4;21(1):321. doi: 10.1186/s12931-020-01537-3. Respir Res. 2020. PMID: 33276795 Free PMC article.
-
[Serum chitotriosidase activity as a biomarker of pulmonary sarcoidosis].Pol Merkur Lekarski. 2011 Sep;31(183):179-82. Pol Merkur Lekarski. 2011. PMID: 21991850 Review. Polish.
-
Serum markers for the staging of disease activity of sarcoidosis and other interstitial lung diseases of unknown etiology.Sarcoidosis Vasc Diffuse Lung Dis. 1998 Mar;15(1):22-37. Sarcoidosis Vasc Diffuse Lung Dis. 1998. PMID: 9571999 Review.
Cited by
-
Identification and validation of hub differential genes in pulmonary sarcoidosis.Front Immunol. 2024 Sep 19;15:1466029. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1466029. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39364409 Free PMC article.
-
Mucopolysaccharidosis Type IVA: Extracellular Matrix Biomarkers in Cardiovascular Disease.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022 May 10;9:829111. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2022.829111. eCollection 2022. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022. PMID: 35620518 Free PMC article.
-
Biomarkers and molecular endotypes of sarcoidosis: lessons from omics and non-omics studies.Front Immunol. 2024 Jan 4;14:1342429. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1342429. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38250062 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cathepsin S: investigating an old player in lung disease pathogenesis, comorbidities, and potential therapeutics.Respir Res. 2020 May 12;21(1):111. doi: 10.1186/s12931-020-01381-5. Respir Res. 2020. PMID: 32398133 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Integrative Identification of Hub Genes Associated With Immune Cells in Atrial Fibrillation Using Weighted Gene Correlation Network Analysis.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2021 Jan 21;7:631775. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2020.631775. eCollection 2020. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2021. PMID: 33553270 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hunninghake GW. ATS/ERS/WASOG statement on sarcoidosis. American Thoracic Society/European Respiratory Society/World Association of Sarcoidosis and other Granulomatous Disorders. Sarcoidosis Vasc Diffuse Lung Dis. 1999;16:149–73. - PubMed
-
- Lieberman J. Elevation of serum angiotensin-converting-enzyme (ACE) level in sarcoidosis. Am J Med. 1975;59:365–72. - PubMed
-
- Tsutsumi T, Nagai S, Imai K, Setoyama Y, Uchiyama T, Izumi T. Soluble interleukin-2 receptor in blood from patients with sarcoidosis and idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Sarcoidosis. 1994;11:102–9. - PubMed
-
- Miyoshi S, Hamada H, Kadowaki T, et al. Comparative evaluation of serum markers in pulmonary sarcoidosis. Chest. 2010;137:1391–7. - PubMed
-
- Bargagli E, Mazzi A, Mezzasalma F, et al. The analysis of tryptase in serum of sarcoidosis patients. Inflammation. 2009;32:310–4. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
