Effectiveness and tolerability of methotrexate in pulmonary sarcoidosis: A single center real-world study
- PMID: 32476957
- PMCID: PMC7247084
- DOI: 10.36141/svdld.v36i3.8449
Effectiveness and tolerability of methotrexate in pulmonary sarcoidosis: A single center real-world study
Abstract
Background: Pulmonary sarcoidosis patients who get disease progression despite corticosteroid treatment or can't tolerate corticosteroid required second-line drug. Methotrexate (MTX) is the most widely used in our clinical practice. Data on its safety and efficacy at different doses are still limited, especially for those without folic acid supplements.
Objective: To report effectiveness of different MTX dosages and tolerability of MTX in pulmonary sarcoidosis without folic acid supplements.
Methods: A retrospective study on pulmonary sarcoidosis patients receiving MTX therapy with various dose ≥3 months was conducted. The primary outcome was change in high-resolution computed tomography (HRCT) before and after MTX therapy. Other efficacy parameters included SGRQ score, prednisone dose change, discontinuation and relapse-free survival. Response-linked factors and safety outcomes were also analyzed.
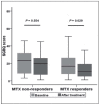
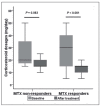
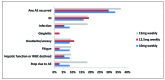
Results: Overall, 49 patients (81.7%) were assessed as MTX responders by HRCT and there was no significant difference in clinical response rate among three groups with different doses. The health-related quality of life (HRQL) of the responders improved obviously, which was evidenced by SGRQ score declining from 16.7(IQR: 7.9-26.4) to 10.7(IQR: 4.8-19.3) (P=0.029). The corticosteroids sparing effect was confirmed in "responders" group (P<0.001). When MTX was discontinued in 11 responders with complete improvement, 2 patients experienced relapses within 15.5 (range: 1-30) months (mean follow-up time of these 11 responders: 13.5±13.0 months). No clinical characteristics were found related to MTX effectiveness. Adverse events occurred in 31.7% of the patients, with gastrointestinal-related being the commonest. Drug discontinuation owing to adverse events occupied 6.7% of the subjects.
Conclusions: Nearly 80% of the sarcoidosis subjects had well response to MTX. Its effectiveness was irrelevant to the treatment dosages and baseline characteristics. A quite low relapse rate was witnessed in those complete responders discontinuing MTX therapies. The steroid-sparing effect, well drug tolerability and low drug withdrawal rate were observed in these patients even without folic acid supplements in clinical practice.
Keywords: effectiveness; methotrexate; sarcoidosis; tolerability.
Copyright: © 2020.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Methotrexate as a single agent for treating pulmonary sarcoidosis: a single centre real-life prospective study.Pneumonol Alergol Pol. 2014;82(6):518-33. doi: 10.5603/PiAP.2014.0069. Pneumonol Alergol Pol. 2014. PMID: 25339562 Clinical Trial.
-
Methotrexate treatment efficacy in sarcoidosis might be related to TNF-α polymorphism: real life preliminary study.Sarcoidosis Vasc Diffuse Lung Dis. 2019;36(4):261-273. doi: 10.36141/svdld.v36i4.7708. Epub 2019 May 1. Sarcoidosis Vasc Diffuse Lung Dis. 2019. PMID: 32476962 Free PMC article.
-
Design of a randomized controlled trial to evaluate effectiveness of methotrexate versus prednisone as first-line treatment for pulmonary sarcoidosis: the PREDMETH study.BMC Pulm Med. 2020 Oct 19;20(1):271. doi: 10.1186/s12890-020-01290-9. BMC Pulm Med. 2020. PMID: 33076885 Free PMC article.
-
What is the future of methotrexate in sarcoidosis? A study and review.Curr Opin Pulm Med. 2002 Sep;8(5):470-6. doi: 10.1097/00063198-200209000-00022. Curr Opin Pulm Med. 2002. PMID: 12172455 Review.
-
Pharmacotherapeutic management of pulmonary sarcoidosis.Am J Respir Med. 2003;2(4):311-20. doi: 10.1007/BF03256659. Am J Respir Med. 2003. PMID: 14719997 Review.
Cited by
-
[Sarcoidosis].Z Rheumatol. 2023 Jun;82(5):389-403. doi: 10.1007/s00393-023-01338-1. Epub 2023 Jun 1. Z Rheumatol. 2023. PMID: 37261551 German.
-
Fibrotic Pulmonary Sarcoidosis-From Pathogenesis to Management.J Clin Med. 2025 Mar 30;14(7):2381. doi: 10.3390/jcm14072381. J Clin Med. 2025. PMID: 40217830 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Repository Corticotropin Injection for the Treatment of Pulmonary Sarcoidosis: A Narrative Review.Pulm Ther. 2022 Mar;8(1):43-55. doi: 10.1007/s41030-022-00181-0. Epub 2022 Feb 3. Pulm Ther. 2022. PMID: 35113366 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cardiac sarcoidosis treated with nonsteroidal immunosuppressive therapy.Int J Cardiol Heart Vasc. 2024 Jul 23;53:101473. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcha.2024.101473. eCollection 2024 Aug. Int J Cardiol Heart Vasc. 2024. PMID: 39139610 Free PMC article.
-
Health-related quality of life in sarcoidosis patients and the effect of occupational exposures: a cross-sectional study.BMC Pulm Med. 2025 Feb 17;25(1):83. doi: 10.1186/s12890-025-03552-w. BMC Pulm Med. 2025. PMID: 39962498 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Iannuzzi MC, Rybicki BA, Teirstein AS. Sarcoidosis. N Engl J Med. [Journal Article; Research Support, N.I.H., Extramural; Review]. 2007. 2007-11-22;357(21):2153–65. - PubMed
-
- Baughman RP, Nunes H. Therapy for sarcoidosis: evidence-based recommendations. Expert Rev Clin Immunol. [Journal Article; Review]. 2012. 2012-01-01;8(1):95–103. - PubMed
-
- Schutt AC, Bullington WM, Judson MA. Pharmacotherapy for pulmonary sarcoidosis: a Delphi consensus study. Respir Med. [Journal Article]. 2010. 2010-05-01;104(5):717–23. - PubMed
-
- Chan ES, Cronstein BN. Methotrexate--how does it really work? Nat Rev Rheumatol. [Review]. 2010. 2010-03-01;6(3):175–8. - PubMed
-
- Baughman RP, Winget DB, Lower EE. Methotrexate is steroid sparing in acute sarcoidosis: results of a double blind, randomized trial. Sarcoidosis Vasc Diffuse Lung Dis. [Clinical Trial; Journal Article; Randomized Controlled Trial]. 2000. 2000-03-01;17(1):60–6. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources