Serum cytokines and their predictive value in pulmonary involvement of systemic sclerosis
- PMID: 32476963
- PMCID: PMC7247092
- DOI: 10.36141/svdld.v36i4.7612
Serum cytokines and their predictive value in pulmonary involvement of systemic sclerosis
Abstract
Objective: To identify serum cytokines which predict mortality and/or disease progression in patients with systemic sclerosis, especially with pulmonary involvement.
Methods: Serum cytokines (IL-6, IL-7, IL-8, IL-10, CCL2, CCL4, TGF-β, TNF-α) were measured in 125 SSc patients, who were recruited and observed in our outpatient clinic. Of these, 60 had pulmonary involvement, classified as either interstitial lung disease (ILD, 43 patients), pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH, 7 patients) or pulmonary hypertension and ILD (PH-ILD, 10 patients). The association of serum cytokines with clinical features was analysed and their correlation with BAL cytokines measured in a subset of SSc patients with ILD.
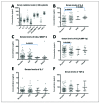
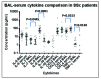
Results: Serum cytokines were detected at different levels: high (TGF-β, median 287.5 pg/ml; CCL2, median 89.7 pg/ml; CCL4, median 104.2 pg/ml), low (IL-6, median 3.2 pg/ml; IL-7 median 2.3 pg/ml; IL-8, median 5.2 pg/ml; TNF-α, median 0 pg/ml but with a bimodal distribution) and very low (IL-10, median 0.4 pg/ml). IL-6 and IL-7 were predictive for death in a Cox regression analysis in all SSc patients as well as in all patients with pulmonary involvement; IL-6 was predictive for mortality in SSc-ILD patients. In a multivariate analysis, cytokine levels could also predict a change in lung function, e.g. IL-7 was a predictor for a decline of diffusion capacity (DLCO) by 20 or 30% in ILD patients. In a subset of ILD patients, serum cytokines were compared to BAL cytokines, but revealed only few correlations.
Conclusion: In conclusion, the analysis of serum cytokines implicates a role as biomarkers, distinct from BAL.
Keywords: chemokines; cytokines; lung involvement; survival; systemic sclerosis.
Copyright: © 2019.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Serum interleukin 6 is predictive of early functional decline and mortality in interstitial lung disease associated with systemic sclerosis.J Rheumatol. 2013 Apr;40(4):435-46. doi: 10.3899/jrheum.120725. Epub 2013 Feb 1. J Rheumatol. 2013. PMID: 23378460
-
Association of elevated α-defensin levels with interstitial pneumonia in patients with systemic sclerosis.Respir Res. 2015 Dec 10;16:148. doi: 10.1186/s12931-015-0308-1. Respir Res. 2015. PMID: 26654954 Free PMC article.
-
Interleukin-17 and interleukin-23: importance in the pathogenesis of lung impairment in patients with systemic sclerosis.Int J Rheum Dis. 2014 Jul;17(6):664-70. doi: 10.1111/1756-185X.12290. Epub 2014 Jan 28. Int J Rheum Dis. 2014. PMID: 24467649
-
Serum concentration of surfactant protein D in patients with systemic sclerosis: The potential marker of the interstitial lung disease severity.Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. 2018 Aug;32(4):541-549. doi: 10.1016/j.berh.2019.01.005. Epub 2019 Feb 14. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. 2018. PMID: 31174823 Review.
-
Review: Serum biomarkers in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and systemic sclerosis associated interstitial lung disease - frontiers and horizons.Pharmacol Ther. 2019 Oct;202:40-52. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2019.05.014. Epub 2019 May 31. Pharmacol Ther. 2019. PMID: 31153954 Review.
Cited by
-
Mediators of systemic sclerosis-associated interstitial lung disease (SSc-ILD): systematic review and meta-analyses.Thorax. 2023 Aug;78(8):799-807. doi: 10.1136/thorax-2022-219226. Epub 2022 Oct 19. Thorax. 2023. PMID: 36261273 Free PMC article.
-
Heterogeneity of determining disease severity, clinical course and outcomes in systemic sclerosis-associated interstitial lung disease: a systematic literature review.RMD Open. 2023 Nov;9(4):e003426. doi: 10.1136/rmdopen-2023-003426. RMD Open. 2023. PMID: 37940340 Free PMC article.
-
CXCL4-RNA Complexes Circulate in Systemic Sclerosis and Amplify Inflammatory/Pro-Fibrotic Responses by Myeloid Dendritic Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Dec 30;24(1):653. doi: 10.3390/ijms24010653. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36614095 Free PMC article.
-
Viewpoint: a multidisciplinary approach to the assessment of patients with systemic sclerosis-associated interstitial lung disease.Clin Rheumatol. 2023 Mar;42(3):653-661. doi: 10.1007/s10067-022-06408-4. Epub 2022 Oct 21. Clin Rheumatol. 2023. PMID: 36271064 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Treatable Traits in Systemic Sclerosis.Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2023 Oct;65(2):251-276. doi: 10.1007/s12016-023-08969-x. Epub 2023 Aug 21. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37603199 Review.
References
-
- Gabrielli A, Avvedimento EV, Krieg T. Scleroderma. N Engl J Med. 2009;360:1989–2003. - PubMed
-
- Gu YS, Kong J, Cheema GS, Keen CL, Wick G, Gershwin ME. The immunobiology of systemic sclerosis. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2008;38:132–60. - PubMed
-
- Katsumoto TR, Whitfield ML, Connolly MK. The pathogenesis of systemic sclerosis. Annu Rev Pathol. 2011;6:509–37. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
