Absence of Rhythm Benefit on Speech in Noise Recognition in Children Diagnosed With Auditory Processing Disorder
- PMID: 32477048
- PMCID: PMC7232546
- DOI: 10.3389/fnins.2020.00418
Absence of Rhythm Benefit on Speech in Noise Recognition in Children Diagnosed With Auditory Processing Disorder
Abstract
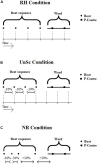
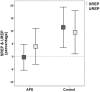
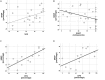
Auditory processing disorder (APD) is a specific deficit in the processing of auditory information along the central auditory nervous system. It is characterized mainly by deficits in speech in noise recognition. APD children may also present with deficits in processing of auditory rhythm. Rhythmic neural entrainment is commonly present in perception of both speech and music, while auditory rhythmic priming of speech in noise has been known to enhance recognition in typical children. Here, we test the hypothesis that the effect of rhythmic priming is compromised in APD children, and further assessed for correlations with verbal and non-verbal auditory processing and cognition. Forty APD children and 33 neurotypical ones were assessed through (a) WRRC, a test measuring the effects of rhythmic priming on speech in noise recognition, (b) a battery of auditory processing tests, commonly used in APD diagnosis, and (c) two cognitive tests, assessing working memory and auditory attention respectively. Findings revealed that (a) the effect of rhythmic priming on speech in noise recognition is absent in APD children, (b) it is linked to non-verbal auditory processing, and (c) it is only weakly dependent on cognition. We discuss these findings in light of Dynamic Attention Theory, neural entrainment and neural oscillations and suggest that these functions may be compromised in APD children. Further research is needed (a) to explore the nature of the mechanics of rhythmic priming on speech in noise perception and why the effect is absent in APD children, (b) which other mechanisms related to both rhythm and language are also affected in this population, and (c) whether music/rhythm training can restore deficits in rhythm effects.
Keywords: auditory processing disorder; cognition; dynamic attending theory; hearing; neural entrainment; rhythm.
Copyright © 2020 Sidiras, Iliadou, Nimatoudis and Bamiou.
Figures
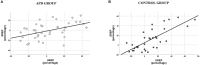
Similar articles
-
Deficits in Auditory Rhythm Perception in Children With Auditory Processing Disorder Are Unrelated to Attention.Front Neurosci. 2019 Sep 6;13:953. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2019.00953. eCollection 2019. Front Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 31551701 Free PMC article.
-
Spectro-temporal modulation detection and its relation to speech perception in children with auditory processing disorder.Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2020 Apr;131:109860. doi: 10.1016/j.ijporl.2020.109860. Epub 2020 Jan 3. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2020. PMID: 31958768
-
Auditory processing disorder in children: the value of a multidisciplinary assessment.Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2021 Dec;278(12):4749-4756. doi: 10.1007/s00405-020-06601-8. Epub 2021 Jan 18. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2021. PMID: 33462745
-
Same or Different: The Overlap Between Children With Auditory Processing Disorders and Children With Other Developmental Disorders: A Systematic Review.Ear Hear. 2018 Jan/Feb;39(1):1-19. doi: 10.1097/AUD.0000000000000479. Ear Hear. 2018. PMID: 28863035 Free PMC article.
-
Processing rhythm in speech and music: Shared mechanisms and implications for developmental speech and language disorders.Neuropsychology. 2021 Nov;35(8):771-791. doi: 10.1037/neu0000766. Epub 2021 Aug 26. Neuropsychology. 2021. PMID: 34435803 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Auditory Processing in Musicians, a Cross-Sectional Study, as a Basis for Auditory Training Optimization.Healthcare (Basel). 2023 Jul 14;11(14):2027. doi: 10.3390/healthcare11142027. Healthcare (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37510468 Free PMC article.
-
Acupuncture might enhance word recognition scores in a patient with hearing loss: a case report and literature review.Front Neurosci. 2025 May 15;19:1593659. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2025.1593659. eCollection 2025. Front Neurosci. 2025. PMID: 40443804 Free PMC article.
-
On the Difference of Scoring in Speech in Babble Tests.Healthcare (Basel). 2022 Feb 28;10(3):458. doi: 10.3390/healthcare10030458. Healthcare (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35326936 Free PMC article.
References
-
- American Academy of Audiology [AAA] (2010). Diagnosis, Treatment and Management of Children and Adults with Central Auditory Processing Disorder. Available online at: https://audiology-web.s3.amazonaws.com/migrated/CAPD%20Guidelines%208-20... (accessed September 12, 2019).
-
- American Speech-Language-Hearing Association [ASHA] (2005). Central Auditory Processing Disorders. Available from: http://www.asha.org/policy/TR2005-00043/
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

