Serum Amyloid A1 (SAA1) Revisited: Restricted Leukocyte-Activating Properties of Homogeneous SAA1
- PMID: 32477346
- PMCID: PMC7240019
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.00843
Serum Amyloid A1 (SAA1) Revisited: Restricted Leukocyte-Activating Properties of Homogeneous SAA1
Abstract
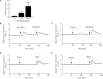
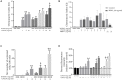
Infection, sterile injury, and chronic inflammation trigger the acute phase response in order to re-establish homeostasis. This response includes production of positive acute phase proteins in the liver, such as members of the serum amyloid A (SAA) family. In humans the major acute phase SAAs comprise a group of closely related variants of SAA1 and SAA2. SAA1 was proven to be chemotactic for several leukocyte subtypes through activation of the G protein-coupled receptor FPRL1/FPR2. Several other biological activities of SAA1, such as cytokine induction, reported to be mediated via TLRs, have been debated recently. Especially commercial SAA1, recombinantly produced in Escherichia coli, was found to be contaminated with bacterial products confounding biological assays performed with this rSAA1. We purified rSAA1 by RP-HPLC to homogeneity, removing contaminants such as lipopolysaccharides, lipoproteins and formylated peptides, and re-assessed several biological activities attributed to SAA1 (chemotaxis, cytokine induction, MMP-9 release, ROS generation, and macrophage differentiation). The homogeneous rSAA1 (hrSAA1) lacked most cell-activating properties, but its leukocyte-recruiting capacity in vivo and it's in vitro synergy with other leukocyte attractants remained preserved. Furthermore, hrSAA1 maintained the ability to promote monocyte survival. This indicates that pure hrSAA1 retains its potential to activate FPR2, whereas TLR-mediated effects seem to be related to traces of bacterial TLR ligands in the E. coli-produced human rSAA1.
Keywords: FPR2; MMP-9; ROS; SAA; chemokines; chemotaxis; macrophages; neutrophils.
Copyright © 2020 Abouelasrar Salama, De Bondt, De Buck, Berghmans, Proost, Oliveira, Amaral, Gouwy, Van Damme and Struyf.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Matrix Metalloproteinase-9-Generated COOH-, but Not NH2-Terminal Fragments of Serum Amyloid A1 Retain Potentiating Activity in Neutrophil Migration to CXCL8, With Loss of Direct Chemotactic and Cytokine-Inducing Capacity.Front Immunol. 2018 Jun 4;9:1081. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.01081. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29915572 Free PMC article.
-
Serum amyloid A1 isoforms display different efficacy at Toll-like receptor 2 and formyl peptide receptor 2.Immunobiology. 2014 Dec;219(12):916-23. doi: 10.1016/j.imbio.2014.08.002. Epub 2014 Aug 10. Immunobiology. 2014. PMID: 25154907 Free PMC article.
-
COOH-terminal SAA1 peptides fail to induce chemokines but synergize with CXCL8 and CCL3 to recruit leukocytes via FPR2.Blood. 2018 Jan 25;131(4):439-449. doi: 10.1182/blood-2017-06-788554.. Blood. 2018. PMID: 29371208
-
Functional Interactions Between Recombinant Serum Amyloid A1 (SAA1) and Chemokines in Leukocyte Recruitment.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Mar 3;26(5):2258. doi: 10.3390/ijms26052258. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40076881 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Acute-serum amyloid A and A-SAA-derived peptides as formyl peptide receptor (FPR) 2 ligands.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023 Feb 3;14:1119227. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1119227. eCollection 2023. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 36817589 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Biological Characterization of Commercial Recombinantly Expressed Immunomodulating Proteins Contaminated with Bacterial Products in the Year 2020: The SAA3 Case.Mediators Inflamm. 2020 Jul 6;2020:6087109. doi: 10.1155/2020/6087109. eCollection 2020. Mediators Inflamm. 2020. PMID: 32694927 Free PMC article.
-
Cell-Specific Regulation of Inflammatory Cytokines and Acute-Phase Proteins by the Glucocorticoid Receptor.Mediators Inflamm. 2023 Nov 28;2023:4399998. doi: 10.1155/2023/4399998. eCollection 2023. Mediators Inflamm. 2023. PMID: 39619227 Free PMC article.
-
Serum amyloid A is a positive acute phase protein in Russian sturgeon challenged with Aeromonas hydrophila.Sci Rep. 2020 Dec 17;10(1):22162. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-79065-9. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 33335147 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of crucial genes that induce coronary atherosclerosis through endothelial cell dysfunction in AMI-identifying hub genes by WGCNA.Am J Transl Res. 2022 Nov 15;14(11):8166-8174. eCollection 2022. Am J Transl Res. 2022. PMID: 36505315 Free PMC article.
-
The turning away of serum amyloid A biological activities and receptor usage.Immunology. 2021 Jun;163(2):115-127. doi: 10.1111/imm.13295. Epub 2021 Jan 4. Immunology. 2021. PMID: 33315264 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Saranya Revathy K, Umasuthan N, Whang I, Lee Y, Lee S, Oh MJ, et al. A novel acute phase reactant, serum amyloid A-like 1, from Oplegnathus fasciatus: genomic and molecular characterization and transcriptional expression analysis. Dev Comp Immunol. (2012) 37:294–305. 10.1016/j.dci.2012.03.014 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

