How Attentional Guidance and Response Selection Boost Contextual Learning: Evidence from Eye Movement
- PMID: 32477438
- PMCID: PMC7246933
- DOI: 10.5709/acp-0274-2
How Attentional Guidance and Response Selection Boost Contextual Learning: Evidence from Eye Movement
Abstract
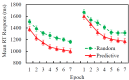
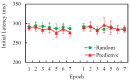
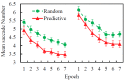
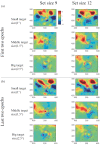
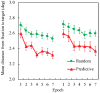
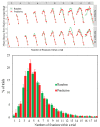
The contextual cueing effect (CCE) refers to the learned association between predictive configuration and target location, speeding up response times for targets. Previous studies have examined the underlying processes (initial perceptual process, attentional guidance, and response selection) of CCE but have not reached a general consensus on their contributions to CCE. In the present study, we used eye tracking to address this question by analyzing the oculomotor correlates of context-guided learning in visual search and eliminating indefinite response factors during response priming. The results show that both attentional guidance and response selection contribute to contextual learning.
Keywords: attentional guidance; contextual cueing effect; eye movement; response selection.
Copyright: © 2019 University of Economics and Human Sciences in Warsaw.
Figures


References
-
- Beesley T., Vadillo M. A., Pearson D., Shanks D. R. Pre-exposure of repeated search configurations facilitates subsequent contextual cuing of visual search. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Learning, Memory, and Cognition. 2015;41:348–362. - PubMed
-
- Beesley T., Hanafi G., Vadillo, M. A., Shanks D. R., Livesey E. J. Overt attention in contextual cuing of visual search is driven by the attentional set, but not by the predictiveness of distractors. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Learning, Memory,and Cognition, 2018;44:707–721. - PubMed
-
- Caldara R., Miellet S. iMap: a novel method for statistical fixation mapping of eye movement data. Behavior Research Methods. 2011;43:864–878. - PubMed
-
- Chun M. M., Jiang Y. H. Contextual cueing: Implicit learning and memory of visual context guides spatial attention. Cognitive Psychology. 1998;36:28–71. - PubMed
-
- Chun M. M., Jiang Y. H. Top-down attentional guidance based on implicit learning of visual covariation. Psychological Science. 1999;10:360–365.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
