A report of two challenging cases of bone infection: Mycobacterium tuberculosis. How to manage?
- PMID: 32477575
- PMCID: PMC7243712
- DOI: 10.1093/omcr/omaa025
A report of two challenging cases of bone infection: Mycobacterium tuberculosis. How to manage?
Abstract
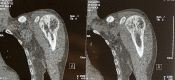
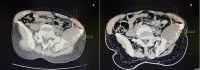
The incidence of bone tuberculosis is less than 5% of all tuberculosis cases. Furthermore, multifocal bone tuberculosis is uncommon, which rarely occurs without primary foci. It is difficult to diagnose, particularly if it is localized in both humeral heads. On the other hand, the isolated iliac bone tuberculosis is exceptional; it constitutes, also, a challenging diagnosis, which requires a high index of clinical suspicion and advanced investigations. Herein, we first report a case of multifocal tuberculosis of both humeral heads with no primary foci, and we secondarily report a case of isolated iliac bone tuberculosis. At last, however, the histological exam and polymerase chain reaction for the Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex are not always positives; they are mandatory as tests to ascertain the diagnosis.
Keywords: anti-bacillary; bone tuberculosis; polymerase chain reaction.
© The Author(s) 2020. Published by Oxford University Press.
Figures




References
-
- Stingo FE, Rodriguez-Fontan F, Burger-Van der Walt E, Arce J, Garcia SN, Munafo RM. Isolated iliac crest tuberculosis: a case report. JBJS Case Connect 2018;8:e31. - PubMed
-
- Yilmaz MH, Kantarci F, Mihmanli I, Kanberoglu K. Multifocal skeletal tuberculosis. South Med J 2004;97:785–7. - PubMed
-
- Davidson PT, Horowitz I. Skeletal tuberculosis: a review with patient presentations and discussion. Am J Med 1970;48:77–84. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

