Current status of imaging diagnosis in the transplanted kidney. A review of the literature with a special focus on contrast-enhanced ultrasonography
- PMID: 32478319
- PMCID: PMC7243885
- DOI: 10.15386/mpr-1536
Current status of imaging diagnosis in the transplanted kidney. A review of the literature with a special focus on contrast-enhanced ultrasonography
Abstract
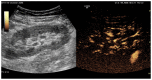
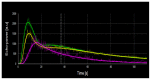
Objectives: Ultrasonographic scanning is currently the most widespread imaging diagnostic procedure. The method provides real-time morphological, vascular and elastographic information in a non-invasive manner. In recent years, harmonic vascular examination has become accessible using intravenous contrast agents. In urological pathology, this procedure is used in the detection and evaluation of vascular and ischemic complications, in the classification of complex cysts according to the Bosniak system, also in the renal lesions with uncertain etiology and in acute pyelonephritis for the detection of abscesses. The contrast agent (SonoVue) is angiospecific and can be used in patients transplanted immediately after surgery without adverse effects or impaired renal function. Thus, it is desirable to be used in the nephrological pathology of the renal graft and to develop diagnostic models based on the evaluation of renal microvascularization, as well as the quantitative data resulting from the graphical representation of the specific parameters. The purpose of this review is to evaluate the current state of the literature regarding the place and role of contrast substance ultrasound in the early diagnosis of acute renal graft dysfunction and to make a differential diagnosis of this pathological entity.
Method: This review quantifies the role of contrast ultrasound in the diagnosis of acute complications of the renal graft. The research was conducted based on the databases PubMed, MedScape, Cochrane, according to the search criteria such as contrast-enhanced ultrasound + kidney transplant, "time intensity curves" + "kidney transplant", filtered for the period 2004-2018.
Results: In the nephrological pathology of the renal graft, contrast-enhanced ultrasound is a valuable tool, superior to Doppler ultrasound in predicting the evolution of the renal graft, identifying very small early defects in renal microvascularization. A number of studies succeeded in identifying acute graft dysfunction, some of which establish its etiology - humoral rejection versus acute tubular necrosis. On the other hand, the contrast-enhanced ultrasound parameters do not have the ability to distinguish between cellular and humoral rejection.
Conclusions: If, at present, the histopathological examination is the only one that can differentiate with certainty the cause of acute renal graft dysfunction, we consider that contrast-enhanced ultrasound, as a non-invasive imaging technique, opens a favorable perspective for increasing the survival of the renal graft and decreasing the complications in the renal transplant. The combination of other ultrasound techniques, together with contrast-enhanced ultrasound, could lead to the development of new diagnostic models.
Keywords: acute humoral rejection; acute rejection; acute tubular necrosis; contrast-enhanced ultrasound; imaging diagnosis; kidney transplantation; time-intensity curve.
Figures







References
-
- Lim WH, Johnson DW, Teixeira-Pinto A, Wong G. Association between duration of delayed graft function, acute rejection, and allograft outcome after deceased donor kidney transplantation. Transplantation. 2019;103:412–419. - PubMed
-
- Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) Transplant Work Group. KDIGO clinical practice guideline for the care of kidney transplant recipients. Kidney Disease: Improving GlobalOutcomes (KDIGO) Transplant Work Group. Am J Transplant. 2009;9(Suppl 3):S1–S155. - PubMed
-
- Redfield RR, McCune KR, Rao A, Sadowski E, Hanson M, Kolterman AJ, et al. Nature, timing, and severity of complications from ultrasound-guided percutaneous renal transplant biopsy. Transpl Int. 2016;29:167–172. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
