Conformational distributions of isolated myosin motor domains encode their mechanochemical properties
- PMID: 32479265
- PMCID: PMC7259954
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.55132
Conformational distributions of isolated myosin motor domains encode their mechanochemical properties
Abstract
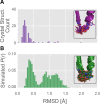
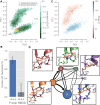
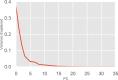
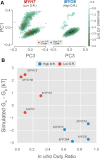
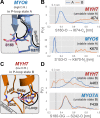
Myosin motor domains perform an extraordinary diversity of biological functions despite sharing a common mechanochemical cycle. Motors are adapted to their function, in part, by tuning the thermodynamics and kinetics of steps in this cycle. However, it remains unclear how sequence encodes these differences, since biochemically distinct motors often have nearly indistinguishable crystal structures. We hypothesized that sequences produce distinct biochemical phenotypes by modulating the relative probabilities of an ensemble of conformations primed for different functional roles. To test this hypothesis, we modeled the distribution of conformations for 12 myosin motor domains by building Markov state models (MSMs) from an unprecedented two milliseconds of all-atom, explicit-solvent molecular dynamics simulations. Comparing motors reveals shifts in the balance between nucleotide-favorable and nucleotide-unfavorable P-loop conformations that predict experimentally measured duty ratios and ADP release rates better than sequence or individual structures. This result demonstrates the power of an ensemble perspective for interrogating sequence-function relationships.
Keywords: biochemistry; chemical biology; chicken; conformational heterogeneity; dictyostelium; energy landscapes; human; machine learning; markov sate models; molecular biophysics; molecular dynamics; structural biology.
© 2020, Porter et al.
Conflict of interest statement
JP, AM, MZ, MG, GB No competing interests declared
Figures
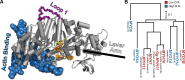

Similar articles
-
Shaking the myosin family tree: biochemical kinetics defines four types of myosin motor.Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2011 Dec;22(9):961-7. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2011.09.015. Epub 2011 Oct 4. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2011. PMID: 22001381 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nucleotide pocket thermodynamics measured by EPR reveal how energy partitioning relates myosin speed to efficiency.J Mol Biol. 2011 Mar 18;407(1):79-91. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2010.11.053. Epub 2010 Dec 23. J Mol Biol. 2011. PMID: 21185304 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamics of myosin-driven skeletal muscle contraction: I. Steady-state force generation.Biophys J. 2005 Jun;88(6):4107-17. doi: 10.1529/biophysj.104.056846. Epub 2005 Mar 18. Biophys J. 2005. PMID: 15778440 Free PMC article.
-
Structural mechanism of the ATP-induced dissociation of rigor myosin from actin.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011 May 10;108(19):7793-8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1018420108. Epub 2011 Apr 25. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011. PMID: 21518908 Free PMC article.
-
Force generation by kinesin and myosin cytoskeletal motor proteins.J Cell Sci. 2013 Jan 1;126(Pt 1):9-19. doi: 10.1242/jcs.103911. Epub 2013 Mar 13. J Cell Sci. 2013. PMID: 23487037 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
SARS-CoV-2 Simulations Go Exascale to Capture Spike Opening and Reveal Cryptic Pockets Across the Proteome.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2020 Oct 7:2020.06.27.175430. doi: 10.1101/2020.06.27.175430. bioRxiv. 2020. Update in: Nat Chem. 2021 Jul;13(7):651-659. doi: 10.1038/s41557-021-00707-0. PMID: 32637963 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Single-molecule mechanics and kinetics of cardiac myosin interacting with regulated thin filaments.Biophys J. 2023 Jun 20;122(12):2544-2555. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2023.05.008. Epub 2023 May 10. Biophys J. 2023. PMID: 37165621 Free PMC article.
-
Toward physics-based precision medicine: Exploiting protein dynamics to design new therapeutics and interpret variants.Protein Sci. 2024 Mar;33(3):e4902. doi: 10.1002/pro.4902. Protein Sci. 2024. PMID: 38358129 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Atomistic basis of force generation, translocation, and coordination in a viral genome packaging motor.Nucleic Acids Res. 2021 Jun 21;49(11):6474-6488. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkab372. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021. PMID: 34050764 Free PMC article.
-
Cardiac myosin contraction and mechanotransduction in health and disease.J Biol Chem. 2021 Nov;297(5):101297. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2021.101297. Epub 2021 Oct 9. J Biol Chem. 2021. PMID: 34634306 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Abraham MJ, Murtola T, Schulz R, Páll S, Smith JC, Hess B, Lindahl E. GROMACS: high performance molecular simulations through multi-level parallelism from laptops to supercomputers. SoftwareX. 2015;1-2:19–25. doi: 10.1016/j.softx.2015.06.001. - DOI
-
- Berendsen HJC, van der Spoel D, van Drunen R. GROMACS: a message-passing parallel molecular dynamics implementation. Computer Physics Communications. 1995;91:43–56. doi: 10.1016/0010-4655(95)00042-E. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

