Using Information Technology to Manage the COVID-19 Pandemic: Development of a Technical Framework Based on Practical Experience in China
- PMID: 32479411
- PMCID: PMC7282474
- DOI: 10.2196/19515
Using Information Technology to Manage the COVID-19 Pandemic: Development of a Technical Framework Based on Practical Experience in China
Abstract
Background: The coronavirus disease (COVID-19) epidemic poses an enormous challenge to the global health system, and governments have taken active preventive and control measures. The health informatics community in China has actively taken action to leverage health information technologies for epidemic monitoring, detection, early warning, prevention and control, and other tasks.
Objective: The aim of this study was to develop a technical framework to respond to the COVID-19 epidemic from a health informatics perspective.
Methods: In this study, we collected health information technology-related information to understand the actions taken by the health informatics community in China during the COVID-19 outbreak and developed a health information technology framework for epidemic response based on health information technology-related measures and methods.
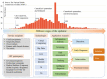
Results: Based on the framework, we review specific health information technology practices for managing the outbreak in China, describe the highlights of their application in detail, and discuss critical issues to consider when using health information technology. Technologies employed include mobile and web-based services such as Internet hospitals and Wechat, big data analyses (including digital contact tracing through QR codes or epidemic prediction), cloud computing, Internet of things, Artificial Intelligence (including the use of drones, robots, and intelligent diagnoses), 5G telemedicine, and clinical information systems to facilitate clinical management for COVID-19.
Conclusions: Practical experience in China shows that health information technologies play a pivotal role in responding to the COVID-19 epidemic.
Keywords: COVID-19; health informatics; health information technology; pandemic; privacy protection; technical framework.
©Qing Ye, Jin Zhou, Hong Wu. Originally published in JMIR Medical Informatics (http://medinform.jmir.org), 08.06.2020.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: None declared.
Figures
References
-
- Lenert L, McSwain BY. Balancing Health Privacy, Health Information Exchange and Research in the Context of the COVID-19 Pandemic. J Am Med Inform Assoc. 2020 Mar 31; doi: 10.1093/jamia/ocaa039. http://europepmc.org/abstract/MED/32232432 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ienca M, Vayena E. On the responsible use of digital data to tackle the COVID-19 pandemic. Nat Med. 2020 Apr;26(4):463–464. doi: 10.1038/s41591-020-0832-5. http://europepmc.org/abstract/MED/32284619 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Reeves JJ, Hollandsworth HM, Torriani FJ, Taplitz R, Abeles S, Tai-Seale M, Millen M, Clay B, Longhurst CA. Rapid Response to COVID-19: Health Informatics Support for Outbreak Management in an Academic Health System. J Am Med Inform Assoc. 2020 Mar 24; doi: 10.1093/jamia/ocaa037. http://europepmc.org/abstract/MED/32208481 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Worldometer. [2020-06-04]. COVID-19 Coronavirus Pandemic https://www.worldometers.info/coronavirus/
-
- Wu JT, Leung K, Leung GM. Nowcasting and forecasting the potential domestic and international spread of the 2019-nCoV outbreak originating in Wuhan, China: a modelling study. Lancet. 2020 Feb;395(10225):689–697. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30260-9. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(20)30260-9. - DOI - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources