Adaptation of codon usage to tRNA I34 modification controls translation kinetics and proteome landscape
- PMID: 32479508
- PMCID: PMC7289440
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1008836
Adaptation of codon usage to tRNA I34 modification controls translation kinetics and proteome landscape
Abstract
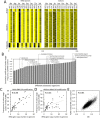
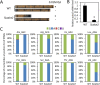
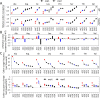
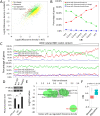
Codon usage bias is a universal feature of all genomes and plays an important role in regulating protein expression levels. Modification of adenosine to inosine at the tRNA anticodon wobble position (I34) by adenosine deaminases (ADATs) is observed in all eukaryotes and has been proposed to explain the correlation between codon usage and tRNA pool. However, how the tRNA pool is affected by I34 modification to influence codon usage-dependent gene expression is unclear. Using Neurospora crassa as a model system, by combining molecular, biochemical and bioinformatics analyses, we show that silencing of adat2 expression severely impaired the I34 modification levels for the ADAT-related tRNAs, resulting in major ADAT-related tRNA profile changes and reprogramming of translation elongation kinetics on ADAT-related codons. adat2 silencing also caused genome-wide codon usage-biased ribosome pausing on mRNAs and proteome landscape changes, leading to selective translational repression or induction of different mRNAs. The induced expression of CPC-1, the Neurospora ortholog of yeast GCN4p, mediates the transcriptional response after adat2 silencing and amino acid starvation. Together, our results demonstrate that the tRNA I34 modification by ADAT plays a major role in driving codon usage-biased translation to shape proteome landscape.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Codon adaptation to tRNAs with Inosine modification at position 34 is widespread among Eukaryotes and present in two Bacterial phyla.RNA Biol. 2018;15(4-5):500-507. doi: 10.1080/15476286.2017.1358348. Epub 2017 Sep 26. RNA Biol. 2018. PMID: 28880718 Free PMC article.
-
The absence of A-to-I editing in the anticodon of plant cytoplasmic tRNA (Arg) ACG demands a relaxation of the wobble decoding rules.RNA Biol. 2012 Oct;9(10):1239-46. doi: 10.4161/rna.21839. Epub 2012 Aug 24. RNA Biol. 2012. PMID: 22922796 Free PMC article.
-
The Expansion of Inosine at the Wobble Position of tRNAs, and Its Role in the Evolution of Proteomes.Mol Biol Evol. 2019 Apr 1;36(4):650-662. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msy245. Mol Biol Evol. 2019. PMID: 30590541
-
Functions and mechanisms of A-to-I RNA editing in filamentous ascomycetes.PLoS Pathog. 2024 Jun 6;20(6):e1012238. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1012238. eCollection 2024 Jun. PLoS Pathog. 2024. PMID: 38843141 Free PMC article. Review.
-
RNA editing by adenosine deaminases generates RNA and protein diversity.Biochimie. 2002 Aug;84(8):791-803. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(02)01446-3. Biochimie. 2002. PMID: 12457566 Review.
Cited by
-
Synonymous but Not Silent: The Codon Usage Code for Gene Expression and Protein Folding.Annu Rev Biochem. 2021 Jun 20;90:375-401. doi: 10.1146/annurev-biochem-071320-112701. Epub 2021 Jan 13. Annu Rev Biochem. 2021. PMID: 33441035 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide profiling of tRNA modifications by Induro-tRNAseq reveals coordinated changes.Nat Commun. 2025 Jan 26;16(1):1047. doi: 10.1038/s41467-025-56348-1. Nat Commun. 2025. PMID: 39865096 Free PMC article.
-
Structural basis for sequence-independent substrate selection by eukaryotic wobble base tRNA deaminase ADAT2/3.Nat Commun. 2022 Nov 8;13(1):6737. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-34441-z. Nat Commun. 2022. PMID: 36347890 Free PMC article.
-
Nonoptimal Codon Usage Is Critical for Protein Structure and Function of the Master General Amino Acid Control Regulator CPC-1.mBio. 2020 Oct 13;11(5):e02605-20. doi: 10.1128/mBio.02605-20. mBio. 2020. PMID: 33051373 Free PMC article.
-
Inosine in Biology and Disease.Genes (Basel). 2021 Apr 19;12(4):600. doi: 10.3390/genes12040600. Genes (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33921764 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

