Protrudin-mediated ER-endosome contact sites promote MT1-MMP exocytosis and cell invasion
- PMID: 32479595
- PMCID: PMC7401796
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.202003063
Protrudin-mediated ER-endosome contact sites promote MT1-MMP exocytosis and cell invasion
Abstract
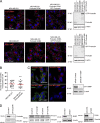
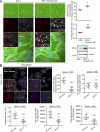
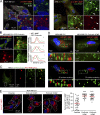
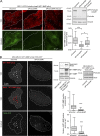
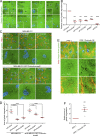
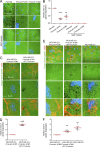
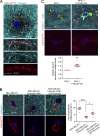
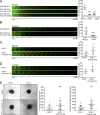
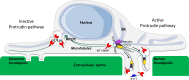
Cancer cells break tissue barriers by use of small actin-rich membrane protrusions called invadopodia. Complete invadopodia maturation depends on protrusion outgrowth and the targeted delivery of the matrix metalloproteinase MT1-MMP via endosomal transport by mechanisms that are not known. Here, we show that the ER protein Protrudin orchestrates invadopodia maturation and function. Protrudin formed contact sites with MT1-MMP-positive endosomes that contained the RAB7-binding Kinesin-1 adaptor FYCO1, and depletion of RAB7, FYCO1, or Protrudin inhibited MT1-MMP-dependent extracellular matrix degradation and cancer cell invasion by preventing anterograde translocation and exocytosis of MT1-MMP. Moreover, when endosome translocation or exocytosis was inhibited by depletion of Protrudin or Synaptotagmin VII, respectively, invadopodia were unable to expand and elongate. Conversely, when Protrudin was overexpressed, noncancerous cells developed prominent invadopodia-like protrusions and showed increased matrix degradation and invasion. Thus, Protrudin-mediated ER-endosome contact sites promote cell invasion by facilitating translocation of MT1-MMP-laden endosomes to the plasma membrane, enabling both invadopodia outgrowth and MT1-MMP exocytosis.
© 2020 Pedersen et al.
Figures

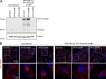
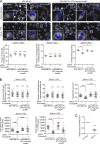
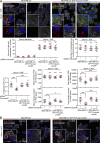
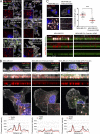
Comment in
-
Protrudin in protrudinG invadopodia: Membrane contact sites and cell invasion.J Cell Biol. 2020 Aug 3;219(8):e202006146. doi: 10.1083/jcb.202006146. J Cell Biol. 2020. PMID: 32692799 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Artym V.V., Zhang Y., Seillier-Moiseiwitsch F., Yamada K.M., and Mueller S.C.. 2006. Dynamic interactions of cortactin and membrane type 1 matrix metalloproteinase at invadopodia: defining the stages of invadopodia formation and function. Cancer Res. 66:3034–3043. 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-05-2177 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

