Clindamycin-induced acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis: A case report
- PMID: 32481338
- PMCID: PMC7249952
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000020389
Clindamycin-induced acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis: A case report
Abstract
Rationale: Acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis (AGEP) is a severe pustular cutaneous adverse drug reaction. Sterile, non-follicular pustules overlying the erythematous skin characterize this reaction.
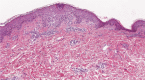
Patient concerns: A 30-year-old Asian women presented with sterile, non-follicular lesions with pus-fluid levels on her back 2 days after taking clindamycin. Skin biopsy revealed a spongiotic change in the epidermis with a focal subcorneal pustule and perivascular eosinophil and lymphocyte infiltration.
Diagnosis: Clindamycin-induced AGEP.
Interventions: We discontinued clindamycin treatment and prescribed systemic corticosteroids.
Outcomes: The pustule stopped spreading within 1 day and the rash improved within 2 days.
Lessons: AGEP is a pustular cutaneous adverse drug reaction that can appear with pus-fluid levels, clinically mimicking Sneddon-Wilkinson disease. The differentiation between both conditions is a history of drug use, characteristic skin lesions and histopathology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors state that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Hotz C, Valeyrie-Allanore L, Haddad C, et al. Systemic involvement of acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis: a retrospective study on 58 patients. Br J Dermatol 2013;169:1223–32. - PubMed
-
- Alniemi DT, Wetter DA, Bridges AG, et al. Acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis: clinical characteristics, etiologic associations, treatments, and outcomes in a series of 28 patients at Mayo Clinic, 1996-2013. Int J Dermatol 2017;56:405–14. - PubMed
-
- Jones JK. Adverse drug reactions in the community health setting: approaches to recognizing, counseling, and reporting. Fam Community Health 1982;5:58–67. - PubMed
-
- Smeets TJ, Jessurun N, Härmark L, et al. Clindamycin-induced acute generalised exanthematous pustulosis: five cases and a review of the literature. Neth J Med 2016;74:421–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

