Precision therapeutic opioid dosing implications from genetic biomarkers and craving score
- PMID: 32481444
- PMCID: PMC12245365
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000020429
Precision therapeutic opioid dosing implications from genetic biomarkers and craving score
Abstract
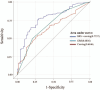
Determining the clinically optimal dose in methadone maintenance therapy (MMT) is a time-consuming procedure, which considers clinical signs and symptoms.To perform a quantitative trait locus association for identifying genetic variants for MMT dosage that underlie heroin addiction and methadone metabolism and then integrate several genotypic and phenotypic factors are potential predictors for clinically optimal MMT dose for personalized prescription.In total, 316 heroin-dependent patients undergoing MMT were recruited at the Addiction Center of the China Medical University Hospital. A multinomial logistic regression model was used to assess associations between genetic polymorphisms and MMT dosing. The data were randomly separated into training and testing sets. In order to enhance the prediction accuracy and the reliability of the prediction model, we used areas under the receiver operating characteristic curves to evaluate optimal MMT dose in both training and testing sets.Four single nucleotide polymorphisms, namely rs806368 in CNR1, s1386493 in TPH2, s16974799 in CYP2B6, and rs2229205 in OPRL1, were significantly associated with the maximum MMT dose (P < .05). The genetic risk score (GRS) was associated with maximum MMT dose, and after adjustments for age, sex, and body mass index, the GRS remained independently associated with the maximum MMT dose. The area under the receiver operating characteristic curve of the combined GRS and craving score was 0.77 for maximum MMT dose, with 75% sensitivity and 60% specificity.Integrating the GRS and craving scores may be useful in the evaluation of individual MMT dose requirements at treatment initiation. Optimal dose prediction allows clinicians to tailor MMT to each patient's needs.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Methadone and buprenorphine for the management of opioid dependence: a systematic review and economic evaluation.Health Technol Assess. 2007 Mar;11(9):1-171, iii-iv. doi: 10.3310/hta11090. Health Technol Assess. 2007. PMID: 17313907
-
Methadone at tapered doses for the management of opioid withdrawal.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2002;(2):CD003409. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003409. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2002. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2003;(2):CD003409. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003409. PMID: 12076479 Updated.
-
Methadone at tapered doses for the management of opioid withdrawal.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2003;(3):CD003409. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003409. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2003. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2004 Oct 18;(4):CD003409. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003409.pub2. PMID: 12917966 Updated.
-
Methadone maintenance at different dosages for opioid dependence.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2003;(3):CD002208. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD002208. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2003. PMID: 12917925
-
Methadone dose in heroin-dependent patients: role of clinical factors, comedications, genetic polymorphisms and enzyme activity.Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2015 Jun;79(6):967-77. doi: 10.1111/bcp.12576. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2015. PMID: 25556837 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Molecular Alterations of the Endocannabinoid System in Psychiatric Disorders.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Apr 26;23(9):4764. doi: 10.3390/ijms23094764. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35563156 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Oueslati B, Moula O, Ghachem R. The impact of OPRM1's genetic polymorphisms on methadone maintenance treatment in opioid addicts: a systematic review. Pharmacogenomics 2018;19:741–7. - PubMed
-
- Maxwell S, Shinderman MS. Optimizing long-term response to methadone maintenance treatment: a 152-week follow-up using higher-dose methadone. J Addict Dis 2002;21:1–2. - PubMed
-
- Kreek MJ, Bart G, Lilly C, et al. Pharmacogenetics and human molecular genetics of opiate and cocaine addictions and their treatments. Pharmacol Rev 2005;57:1–26. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases