No evidence of severe acute respiratory syndrome-coronavirus 2 in semen of males recovering from coronavirus disease 2019
- PMID: 32482249
- PMCID: PMC7164916
- DOI: 10.1016/j.fertnstert.2020.04.024
No evidence of severe acute respiratory syndrome-coronavirus 2 in semen of males recovering from coronavirus disease 2019
Abstract
Objective: To describe detection of severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS)-coronavirus 2 (CoV-2) in seminal fluid of patients recovering from coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) and to describe the expression profile of angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) and Transmembrane Serine Protease 2 (TMPRSS2) within the testicle.
Design: Observational, cross-sectional study.
Setting: Tertiary referral center.
Patient(s): Thirty-four adult Chinese males diagnosed with COVID-19 through confirmatory quantitative reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) from pharyngeal swab samples.
Intervention(s): None.
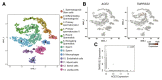
Main outcome measure(s): Identification of SARS-CoV-2 on qRT-PCR of single ejaculated semen samples. Semen quality was not assessed. Expression patterns of ACE2 and TMPRSS2 in the human testis are explored through previously published single-cell transcriptome datasets.
Result(s): Six patients (19%) demonstrated scrotal discomfort suggestive of viral orchitis around the time of COVID-19 confirmation. Severe acute respiratory syndrome-CoV-2 was not detected in semen after a median of 31 days (interquartile range, 29-36 days) from COVID-19 diagnosis. Single-cell transcriptome analysis demonstrates sparse expression of ACE2 and TMPRSS2, with almost no overlapping gene expression.
Conclusion(s): Severe acute respiratory syndrome-CoV-2 was not detected in the semen of patients recovering from COVID-19 1 month after COVID-19 diagnosis. Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2-mediated viral entry of SARS-CoV-2 into target host cells is unlikely to occur within the human testicle based on ACE2 and TMPRSS2 expression. The long-term effects of SARS-CoV-2 on male reproductive function remain unknown.
No hay evidencia de síndrome respiratorio agudo severo - coronavirus 2 en semen de varones que se recuperan de la enfermedad del coronavirus 2019
Objetivo: Describir la detección del síndrome respiratorio agudo severo (SRAS) –coronavirus 2 (CoV-2) en el líquido seminal de pacientes en recuperación de la enfermedad por coronavirus 2019 (COVID-19) y describir el perfil de expresión de la enzima convertidora de angiotensina 2 (ACE2) y Serina Proteasa Transmembrana 2 (TMPRSS2) dentro del testículo.
Diseño experimental: Estudio observacional, transversal.
Lugar de realización: Centro de referencia terciario.
Pacientes: Treinta y cuatro varones chinos adultos diagnosticados con COVID-19 mediante la confirmación cuantitativa de la reacción en cadena de la polimerasa con transcriptasa reversa (qRT-PCR) de muestras de hisopado faríngeo.
Intervenciones: Ninguna.
Principal variable de medida: Identificación de SARS-CoV-2 a través de qRT-PCR de muestras de semen eyaculadas individuales. La calidad del semen no fue evaluada. Los patrones de expresión de ACE2 y TMPRSS2 en los testículos humanos se exploran a través de conjunto de datos de transcriptoma de célula única publicados previamente.
Resultados: Seis pacientes (19%) demostraron molestias escrotales relacionadas con la orquitis viral en el momento de la confirmación de COVID-19. El síndrome respiratorio agudo severo - CoV-2 no se detectó en semen después de una mediana de 31 días (rango intercuartil, 29-36 días) desde el diagnóstico de COVID-19. El análisis de transcriptoma de célula única demuestra una expresión escasa de ACE2 y TMPRSS2, casi sin expresión de genes superpuestos.
Conclusión: El síndrome respiratorio agudo severo-CoV-2 no se detectó en el semen de pacientes que se recuperaron de COVID-19 1 mes después del diagnóstico. La entrada viral mediada por la enzima convertidora de angiotensina 2 del SARS-CoV-2 en las células huésped diana es poco probable que ocurra dentro del testículo humano basado en la expresión de ACE2 y TMPRSS2. Los efectos a largo plazo del SARS-CoV-2 en la función reproductora masculina sigue siendo desconocida.
Keywords: COVID-19; angiotensin-converting enzyme 2; coronavirus; infertility; male; semen.
Copyright © 2020 American Society for Reproductive Medicine. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- The Center for Systems Science and Engineering, Johns Hopkins. Coronavirus COVID-19 Global Cases. 2020. http://www.arcgis.com/apps/opsdashboard/index.html - /bda7594740fd402994... Available at:
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

