Tocilizumab: A Therapeutic Option for the Treatment of Cytokine Storm Syndrome in COVID-19
- PMID: 32482373
- PMCID: PMC7241374
- DOI: 10.1016/j.arcmed.2020.05.009
Tocilizumab: A Therapeutic Option for the Treatment of Cytokine Storm Syndrome in COVID-19
Abstract
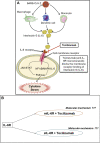
Presently, we need more therapeutic molecules for this COVID-19 outbreak. The severity and mortality of the disease is associated with a high level of release of cytokine in the patients which is known as CRS (cytokine release syndrome) or cytokine storm syndrome. IL-6 is a type of pro-inflammatory cytokine which release in the severe COVID-19 patients. This cytokine initiates CRS the JAK-STAT or MAPK/NF-κB-IL-6 pathway. Tocilizumab, a humanized monoclonal antibody, is designed to bind both mIL-6R (membrane bound receptor for IL-6) and sIL-6R (soluble receptor for IL-6) and inhibit the JAK-STAT or MAPK/NF-κB-IL-6 signaling pathway. It finally stops the cytokine storm syndrome. However, we need to understand that how tocilizumab is bound with mIL-6R or sIL-6R. Similarly, we also need to understand more about the real molecular mechanism of activity of tocilizumab.
Keywords: COVID-19; Cytokine storm syndrome; Therapeutic option; Tocilizumab.
Copyright © 2020 IMSS. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Cytokine release syndrome in severe COVID-19: interleukin-6 receptor antagonist tocilizumab may be the key to reduce mortality.Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2020 May;55(5):105954. doi: 10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.105954. Epub 2020 Mar 29. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2020. PMID: 32234467 Free PMC article.
-
COVID-19: Consider IL-6 receptor antagonist for the therapy of cytokine storm syndrome in SARS-CoV-2 infected patients.J Med Virol. 2020 Nov;92(11):2260-2262. doi: 10.1002/jmv.26078. Epub 2020 Jun 19. J Med Virol. 2020. PMID: 32462717 Free PMC article.
-
Treat 2019 novel coronavirus (COVID-19) with IL-6 inhibitor: Are we already that far?Drug Discov Ther. 2020;14(2):100-102. doi: 10.5582/ddt.2020.03006. Drug Discov Ther. 2020. PMID: 32378647
-
The COVID-19 Cytokine Storm; What We Know So Far.Front Immunol. 2020 Jun 16;11:1446. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.01446. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32612617 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Rational Use of Tocilizumab in the Treatment of Novel Coronavirus Pneumonia.Clin Drug Investig. 2020 Jun;40(6):511-518. doi: 10.1007/s40261-020-00917-3. Clin Drug Investig. 2020. PMID: 32337664 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A metabolic modeling approach reveals promising therapeutic targets and antiviral drugs to combat COVID-19.Sci Rep. 2021 Jun 7;11(1):11982. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-91526-3. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34099831 Free PMC article.
-
Are Antisense Long Non-Coding RNA Related to COVID-19?Biomedicines. 2022 Nov 1;10(11):2770. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10112770. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 36359290 Free PMC article.
-
Nanomaterial-based drug delivery systems as promising carriers for patients with COVID-19.RSC Adv. 2021 Aug 2;11(43):26463-26480. doi: 10.1039/d1ra04835j. eCollection 2021 Aug 2. RSC Adv. 2021. PMID: 35480012 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Combination therapies for COVID-19: An overview of the clinical trials landscape.Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2022 Feb;88(4):1590-1597. doi: 10.1111/bcp.15089. Epub 2021 Oct 17. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 34558094 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Microstructure, pathophysiology, and potential therapeutics of COVID-19: A comprehensive review.J Med Virol. 2021 Jan;93(1):275-299. doi: 10.1002/jmv.26254. Epub 2020 Jul 15. J Med Virol. 2021. PMID: 32617987 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Chakraborty C., Sharma A.R., Bhattacharya M. The 2019 novel coronavirus disease (COVID-19) pandemic: A zoonotic prospective. Asian Pac J Trop Med. 2020:1–5. doi: 10.4103/1995-7645.281613. - DOI
-
- Chakraborty C., Sharma A., Sharma G. SARS-CoV-2 causing pneumonia-associated respiratory disorder (COVID-19): diagnostic and proposed therapeutic options. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2020;24:4016–4026. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials