Progress toward understanding chromosome silencing by Xist RNA
- PMID: 32482714
- PMCID: PMC7263139
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.337196.120
Progress toward understanding chromosome silencing by Xist RNA
Abstract
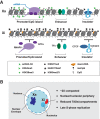
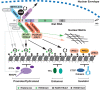
The X inactive-specific transcript (Xist) gene is the master regulator of X chromosome inactivation in mammals. Xist produces a long noncoding (lnc)RNA that accumulates over the entire length of the chromosome from which it is transcribed, recruiting factors to modify underlying chromatin and silence X-linked genes in cis Recent years have seen significant progress in identifying important functional elements in Xist RNA, their associated RNA-binding proteins (RBPs), and the downstream pathways for chromatin modification and gene silencing. In this review, we summarize progress in understanding both how these pathways function in Xist-mediated silencing and the complex interplay between them.
Keywords: LBR; NCoR–HDAC3; Polycomb; RBM15; SPEN; X chromosome inactivation; Xist; chromatin; m6A RNA methylation.
© 2020 Brockdorff et al.; Published by Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press.
Figures


References
-
- Barros de Andrade ESL, Jonkers I, Syx L, Dunkel I, Chaumeil J, Picard C, Foret B, Chen CJ, Lis JT, Heard E, et al. 2019. Kinetics of Xist-induced gene silencing can be predicted from combinations of epigenetic and genomic features. Genome Res 29: 1087–1099. 10.1101/gr.245027.118 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
