Silver nanoparticle conductive inks: synthesis, characterization, and fabrication of inkjet-printed flexible electrodes
- PMID: 32483302
- PMCID: PMC7264204
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-020-65698-3
Silver nanoparticle conductive inks: synthesis, characterization, and fabrication of inkjet-printed flexible electrodes
Abstract
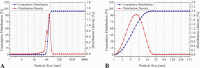
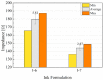
Flexible electronics can be developed with a low-cost and simple fabrication process while being environmentally friendly. Conductive silver inks have been the most applied material in flexible substrates. This study evaluated the performance of different conductive ink formulations using silver nanoparticles by studying the material properties, the inkjet printing process, and application based on electrical impedance spectroscopy using a buffer solution. Silver nanoparticles synthesis was carried out through chemical reduction of silver nitrate; then, seven conductive ink formulations were produced. Properties such as resistivity, viscosity, surface tension, adhesion, inkjet printability of the inks, and electrical impedance of the printed electrodes were investigated. Curing temperature directly influenced the electrical properties of the inks. The resistivity obtained varied from 3.3 × 100 to 5.6 × 10-06 Ω.cm. Viscosity ranged from 3.7 to 7.4 mPa.s, which is suitable for inkjet printing fabrication. By using a buffer solution as an analyte, the printed electrode pairs presented electrical impedance lower than 200 Ω for all the proposed designs, demonstrating the potential of the formulated inks for utilization in flexible electronic devices for biological sensing applications.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
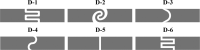






References
-
- Balantrapu, K., McMurran, M. & Goia, D. Inkjet Printing of Silver Nanoparticles for Electronic Applications. Ecadigitallibrary.Com (2010).
-
- Wang Z, et al. Facile synthesis of monodisperse silver nanoparticles for screen printing conductive inks. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2017;28:16939–16947. doi: 10.1007/s10854-017-7614-y. - DOI
-
- Martins, J. P. A. Design and Fabrication by Inkjet Printing of Electrodes for Electromyography. (Universidade de Lisboa, 2013).
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

