Real-time 3D movement correction for two-photon imaging in behaving animals
- PMID: 32483335
- PMCID: PMC7370269
- DOI: 10.1038/s41592-020-0851-7
Real-time 3D movement correction for two-photon imaging in behaving animals
Abstract
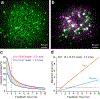
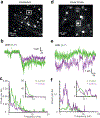
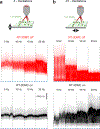
Two-photon microscopy is widely used to investigate brain function across multiple spatial scales. However, measurements of neural activity are compromised by brain movement in behaving animals. Brain motion-induced artifacts are typically corrected using post hoc processing of two-dimensional images, but this approach is slow and does not correct for axial movements. Moreover, the deleterious effects of brain movement on high-speed imaging of small regions of interest and photostimulation cannot be corrected post hoc. To address this problem, we combined random-access three-dimensional (3D) laser scanning using an acousto-optic lens and rapid closed-loop field programmable gate array processing to track 3D brain movement and correct motion artifacts in real time at up to 1 kHz. Our recordings from synapses, dendrites and large neuronal populations in behaving mice and zebrafish demonstrate real-time movement-corrected 3D two-photon imaging with submicrometer precision.
Figures

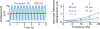





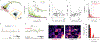
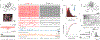
References
-
- Helmchen F. & Denk W. Deep tissue two-photon microscopy. Nat. Methods 2, 932–940 (2005). - PubMed
-
- Svoboda K. & Yasuda R. Principles of Two-Photon Excitation Microscopy and Its Applications to Neuroscience. Neuron 50, 823–839 (2006). - PubMed
-
- Iyer V, Hoogland TM & Saggau P. Fast functional imaging of single neurons using random-access multiphoton (RAMP) microscopy. J. Neurophysiol 95, 535–545 (2006). - PubMed
Methods-only References
-
- Vladimirov N. et al. Light-sheet functional imaging in fictively behaving zebrafish. Nat. Methods 11, 883–884 (2014). - PubMed
-
- Lister JA, Robertson CP, Lepage T, Johnson SL & Raible DW Nacre Encodes a Zebrafish Microphthalmia-Related Protein That Regulates Neural-Crest-Derived Pigment Cell Fate. Development 126, 3757–3767 (1999). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

