Endosteal and periosteal blood flow quantified with dynamic contrast-enhanced fluorescence to guide open orthopaedic surgery
- PMID: 32483397
- PMCID: PMC7263175
- DOI: 10.1117/12.2546173
Endosteal and periosteal blood flow quantified with dynamic contrast-enhanced fluorescence to guide open orthopaedic surgery
Abstract
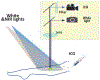
Due to the lack of objectively measurable or quantifiable methods to assess the bone perfusion, the success of removing devitalized bone is based almost entirely on surgeon's experience and varies widely across surgeons and centers. In this study, an indocyanine green (ICG)-based dynamic contrast-enhanced fluorescence imaging (DCE-FI) has been developed to objectively assess bone perfusion and guide surgical debridement. A porcine trauma model (n = 6 pigs × 2 legs) with up to 5 conditions of severity in loss of flow in each, was imaged by a commercial fluorescence imaging system. By applying the bone-specific hybrid plug-compartment (HyPC) kinetic model to four-minute video sequences, the perfusion-related metrics, such as peak intensity, total bone blood flow (TBBF) and endosteal bone blood flow to TBBF fraction (EFF) were calculated. The results shown that the combination of TBBF and EFF can effectively differentiate injured from normal bone with the accuracy, sensitivity and specificity of 89%, 88% and 90%, respectively. Our subsequent first in human bone blood flow imaging study confirmed DCE-FI can be successfully translated into human orthopaedic trauma patients.
Keywords: Boon blood flow; Dynamic contrast-enhanced fluorescence imaging; Indocyanine green; Orthopedic surgery; porcine trauma model.
Figures
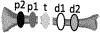
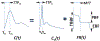
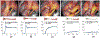
Similar articles
-
ICG-based dynamic contrast-enhanced fluorescence imaging guided open orthopaedic surgery: pilot patient study.Proc SPIE Int Soc Opt Eng. 2021 Mar;11625:116250W. Epub 2021 Mar 5. Proc SPIE Int Soc Opt Eng. 2021. PMID: 36082047 Free PMC article.
-
Bone-specific kinetic model to quantify periosteal and endosteal blood flow using indocyanine green in fluorescence guided orthopedic surgery.J Biophotonics. 2019 Aug;12(8):e201800427. doi: 10.1002/jbio.201800427. Epub 2019 May 8. J Biophotonics. 2019. PMID: 30963727 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of bone perfusion during open orthopedic surgery using quantitative dynamic contrast-enhanced fluorescence imaging.Biomed Opt Express. 2020 Oct 19;11(11):6458-6469. doi: 10.1364/BOE.399587. eCollection 2020 Nov 1. Biomed Opt Express. 2020. PMID: 33282501 Free PMC article.
-
[A new approach for studying the retinal and choroidal circulation].Nippon Ganka Gakkai Zasshi. 2004 Dec;108(12):836-61; discussion 862. Nippon Ganka Gakkai Zasshi. 2004. PMID: 15656089 Review. Japanese.
-
Application of indocyanine green in surgery: A review of current evidence and implementation in trauma patients.World J Gastrointest Surg. 2023 May 27;15(5):757-775. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v15.i5.757. World J Gastrointest Surg. 2023. PMID: 37342859 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Perspective on optical imaging for functional assessment in musculoskeletal extremity trauma surgery.J Biomed Opt. 2020 Aug;25(8):080601. doi: 10.1117/1.JBO.25.8.080601. J Biomed Opt. 2020. PMID: 32869567 Free PMC article.
-
Automated motion artifact correction for dynamic contrast-enhanced fluorescence imaging during open orthopedic surgery.Proc SPIE Int Soc Opt Eng. 2023 Jan-Feb;12361:1236104. doi: 10.1117/12.2650028. Epub 2023 Mar 14. Proc SPIE Int Soc Opt Eng. 2023. PMID: 37034556 Free PMC article.
-
Intraoperative assessment of bone viability through improved analysis and visualization of dynamic contrast-enhanced fluorescence imaging: technique report.OTA Int. 2022 Nov 30;5(4):e222. doi: 10.1097/OI9.0000000000000222. eCollection 2022 Dec. OTA Int. 2022. PMID: 36569105 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ehrlichman L, Rackard F, Sparks M, Harris M, and Gitajn I (2018) Factors associated with treatment failure of implant-related infections in fracture patients. in Orthopaedic Trauma Association Annual Meeting, Orlando, FL
-
- Ovaska MT, Makinen TJ, Madanat R, Vahlberg T, Hirvensalo E, and Lindahl J (2013) Predictors of poor outcomes following deep infection after internal fixation of ankle fractures. Injury 44, 1002–1006 - PubMed
-
- Reilly RM, Robertson T, O’Toole RV, and Manson TT (2016) Are antibiotic nails effective in the treatment of infected tibial fractures? Injury 47, 2809–2815 - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
