The Clinical Drug Ebselen Attenuates Inflammation and Promotes Microbiome Recovery in Mice after Antibiotic Treatment for CDI
- PMID: 32483557
- PMCID: PMC7263476
- DOI: 10.1016/j.xcrm.2020.100005
The Clinical Drug Ebselen Attenuates Inflammation and Promotes Microbiome Recovery in Mice after Antibiotic Treatment for CDI
Abstract
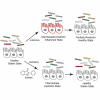
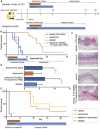
Clostridium difficile infection (CDI) is an enteric bacterial disease that is increasing in prevalence worldwide. C. difficile capitalizes on gut inflammation and microbiome dysbiosis to establish infection, with symptoms ranging from watery diarrhea to toxic megacolon. We reported that the safe-in-human clinical drug ebselen (ClinicalTrials.gov: NCT03013400, NCT01452607, NCT00762671, and NCT02603081) has biochemical, cell-based, and in vivo efficacy against the toxins of C. difficile. Here, we show that ebselen treatment reduces recurrence rates and decreases colitis in a hamster model of relapsing CDI. Furthermore, ebselen treatment does not alter microbiome diversity and promotes recovery back to that of healthy controls after antibiotic-induced dysbiosis in healthy and C. difficile-infected mice. This increased microbiome recovery upon ebselen treatment correlates with a decrease in host-derived inflammatory markers, suggesting that the anti-inflammatory properties of ebselen, combined with its anti-toxin function, help to mitigate the major clinical challenges of CDI, including recurrence, microbial dysbiosis, and colitis.
Conflict of interest statement
DECLARATION OF INTERESTS M.B. is a co-founder, chair of the Scientific Advisory Board and shareholder of Facile Therapeutics, which is a company working to develop ebselen for treatment of CDI. The authors declare a patent application WO2015/200358Al that covers the use of ebselen for treatment of C. difficile infections.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

