Comprehensive database and evolutionary dynamics of U12-type introns
- PMID: 32484558
- PMCID: PMC7367187
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkaa464
Comprehensive database and evolutionary dynamics of U12-type introns
Abstract
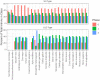
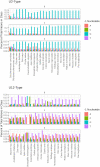
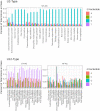
During nuclear maturation of most eukaryotic pre-messenger RNAs and long non-coding RNAs, introns are removed through the process of RNA splicing. Different classes of introns are excised by the U2-type or the U12-type spliceosomes, large complexes of small nuclear ribonucleoprotein particles and associated proteins. We created intronIC, a program for assigning intron class to all introns in a given genome, and used it on 24 eukaryotic genomes to create the Intron Annotation and Orthology Database (IAOD). We then used the data in the IAOD to revisit several hypotheses concerning the evolution of the two classes of spliceosomal introns, finding support for the class conversion model explaining the low abundance of U12-type introns in modern genomes.
© The Author(s) 2020. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
Figures


References
-
- Russell A.G., Charette J.M., Spencer D.F., Gray M.W.. An early evolutionary origin for the minor spliceosome. Nature. 2006; 443:863–866. - PubMed
-
- Hall S.L., Padgett R.A.. Requirement of U12 snRNA for in vivo splicing of a minor class of eukaryotic nuclear pre-mRNA introns. Science. 1996; 271:1716–1718. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

