Tocilizumab challenge: A series of cytokine storm therapy experiences in hospitalized COVID-19 pneumonia patients
- PMID: 32484930
- PMCID: PMC7300754
- DOI: 10.1002/jmv.26111
Tocilizumab challenge: A series of cytokine storm therapy experiences in hospitalized COVID-19 pneumonia patients
Abstract
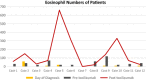
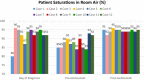
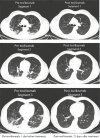
To recognize the period of exaggerated cytokine response in patients with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pneumonia, and to describe the clinical outcomes of using tocilizumab as a treatment option. The data of 12 adult COVID-19 pneumonia patients who were followed in the inpatient clinics of Biruni University Medical Faculty Hospital (Istanbul, Turkey) were retrospectively analyzed. Diagnostic tests, laboratory examinations, clinical findings, and computed tomography of the thorax imaging results were evaluated. A dramatic laboratory and clinical improvement was observed in 83% (10 out of 12) of patients after tocilizumab. In 17% (2 out of 12) of our patients, short-term ventilator support was required in the intensive care unit. The longest hospital stay was 18 days. However, in the end, all of our patients were discharged home with good health. Although arterial oxygen saturations (87.58 ± 3.12%) dropped in room air in the pre-tocilizumab period, post-tocilizumab they normalized in all patients (94.42 ± 1%). None of them had fever after tocilizumab treatment and the levels of C-reactive protein (13.08 ± 12.89) were almost within normal limits. Eosinophil values were quite low at the time of diagnosis (10 ± 17.06), but increased significantly post-tocilizumab (155.33 ± 192.69). There is currently no proven treatment for COVID-19 induced by novel coronavirus SARS-CoV-2. Based on our experience with twelve adult COVID-19 pneumonia patients, we can say that tocilizumab, an IL-6 inhibitor, is more beneficial in preventing the damage caused by excessive cytokine response in the body if administered at the right time and provides clinical and radiological recovery.
Keywords: COVID-19; Pneumonia; SARS-Cov-2; Tocilizumab.
© 2020 Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflict of interests.
Figures
Comment in
-
Tocilizumab's efficacy in patients with Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) is determined by the presence of cytokine storm.J Med Virol. 2021 Jan;93(1):120-121. doi: 10.1002/jmv.26209. Epub 2020 Jun 29. J Med Virol. 2021. PMID: 32568411 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Wuhan Municipal Health Commission. Report of clustering pneumonia of unknown etiology in Wuhan City (published 31 December 2019), 2020.
-
- World Health Organization. Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID‐19): Situation Report—48, 2020.
-
- Gorbalenya AE, Baker SC, Baric RS, et al. Severe acute respiratory syndrome‐related coronavirus—the species and its viruses, a statement of the Coronavirus Study Group. BioRxiv. 2020.
-
- World Health Organization . Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID‐19): Situation Report—22, 2020.
-
- World Health Organization . Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID‐19): Situation Report—51, 2020.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous