Therapeutic index of inhaled corticosteroids in asthma: A dose-response comparison on airway hyperresponsiveness and adrenal axis suppression
- PMID: 32484940
- PMCID: PMC9328361
- DOI: 10.1111/bcp.14406
Therapeutic index of inhaled corticosteroids in asthma: A dose-response comparison on airway hyperresponsiveness and adrenal axis suppression
Abstract
Aims: To compare the airway potency, systemic activity and therapeutic index of three inhaled corticosteroids that differ in glucocorticoid receptor binding affinity, physicochemical and pharmacokinetic properties.
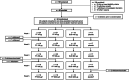
Methods: This escalating-dose, placebo-controlled, cross-over study randomised adults with asthma to 1 or 2 treatment periods with ≥25 days washout in-between. Each treatment period comprised five 7-day dose escalations (μg/d): fluticasone furoate (FF; 25 → 100 → 200 → 400 → 800), fluticasone propionate (FP; 50 → 200 → 500 → 1000 → 2000), budesonide (BUD; 100 → 400 → 800 → 1600 → 3200) or placebo. Airway hyperresponsiveness to adenosine-5'-monophosphate (AMP PC20 ) was assessed on day 8. Plasma cortisol was assessed on day 1 (predose baseline) and from pre-PM dose on day 6 to pre-PM dose day 7 (24-h weighted mean).
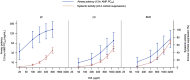
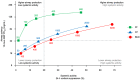
Results: Fifty-four subjects were randomised. FF showed greater airway potency than FP and BUD (AMP PC20 dose at which 50% of the maximum effect is achieved [ED50 ] values: 48.52, 1081.27 and 1467.36 μg/d, respectively). Systemic activity (cortisol suppression) ED50 values were 899.99, 1986.05 and 1927.42 μg/d, respectively. The therapeutic index (ED50 cortisol suppression/ED50 AMP PC20 ) was wider for FF (18.55) than FP (1.84) and BUD (1.31). FF 100 μg/d and 200 μg/d were both comparable in terms of airway potency with high doses of FP (≥1000 μg twice daily [BID]) and BUD (≥1500 μg/BID). The systemic activity of FF 100 μg/d and 200 μg/d (cortisol suppression: 7.41% and 14.28%, respectively) was comparable with low doses of FP (100 μg/BID and 250 μg/BID) and BUD (100 μg/BID and 200 μg/BID).
Conclusion: This study provides evidence that FF can provide more protection against airway hyperresponsiveness, with less systemic activity, than FP or BUD. This suggests that all inhaled corticosteroids are not therapeutically similar and may differ in their therapeutic index. (203162; NCT02991859).
Keywords: AMP challenge; asthma; budesonide; fluticasone furoate; fluticasone propionate; therapeutic index.
© 2020 The Authors. British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of British Pharmacological Society.
Conflict of interest statement
P.D.‐Y., N.Br., S.T., D.A., S.S. and N.Ba. disclose employment with, and stock/share ownership in, GlaxoSmithKline plc. T.H. reports receiving personal fees for advisory boards from GlaxoSmithKline plc., AstraZeneca, Synairgen and Vectura, as well as receiving fees for speaker meetings from AstraZeneca. D.S. reports receiving personal fees from AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Chiesi, Cipla, Genentech, GlaxoSmithKline plc., Glenmark, Menarini, Mundipharma, Novartis, Peptinnovate, Pfizer, Pulmatrix, Theravance and Verona.
Figures
Comment in
-
End-point selection to determine the airway-systemic ratio of inhaled corticosteroids in asthma.Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2021 May;87(5):2401-2402. doi: 10.1111/bcp.14633. Epub 2020 Nov 23. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33230858
References
-
- Global Initiative for Asthma (GINA) . Global Strategy for Asthma Management and Prevention, 2019 update. https://ginasthma.org/wp-content/uploads/2019/06/GINA-2019-main-report-J.... Accessed October 25, 2019.
-
- ARNUITY ELLIPTA (fluticasone furoate inhalation powder), for oral inhalation use . Highlights of prescribing information. Updated June 2019. https://www.gsksource.com/pharma/content/dam/GlaxoSmithKline/US/en/Presc.... Accessed November 27, 2019.
-
- Flixotide 50, 125, 250 micrograms Evohaler . Fluticasone propionate. Summary of product characteristics. Updated 30 October 2019. https://www.medicines.org.uk/emc/product/3824/smpc. Accessed November 27, 2019.
-
- Pulmicort Turbohaler 200 . Budesonide. Summary of product characteristics. Updated 15 June 2017. https://www.medicines.org.uk/emc/product/1385/smpc. Accessed November 27, 2019.

