CD4+ and CD8+ cytotoxic T lymphocytes may induce mesenchymal cell apoptosis in IgG4-related disease
- PMID: 32485263
- PMCID: PMC7704943
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jaci.2020.05.022
CD4+ and CD8+ cytotoxic T lymphocytes may induce mesenchymal cell apoptosis in IgG4-related disease
Abstract
Background: IgG4-related disease (IgG4-RD) is an immune-mediated fibrotic disorder that has been linked to CD4+ cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CD4+CTLs). The effector phenotype of CD4+CTLs and the relevance of both CD8+ cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CD8+CTLs) and apoptotic cell death remain undefined in IgG4-RD.
Objective: We sought to define CD4+CTL heterogeneity, characterize the CD8+CTL response in the blood and in lesions, and determine whether enhanced apoptosis may contribute to the pathogenesis of IgG4-RD.
Methods: Blood analyses were undertaken using flow cytometry, cell sorting, transcriptomic analyses at the population and single-cell levels, and next-generation sequencing for the TCR repertoire. Tissues were interrogated using multicolor immunofluorescence. Results were correlated with clinical data.
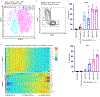
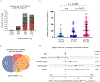
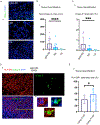
Results: We establish that among circulating CD4+CTLs in IgG4-RD, CD27loCD28loCD57hi cells are the dominant effector subset, exhibit marked clonal expansion, and differentially express genes relevant to cytotoxicity, activation, and enhanced metabolism. We also observed prominent infiltration of granzyme A-expressing CD8+CTLs in disease tissues and clonal expansion in the blood of effector/memory CD8+ T cells with an activated and cytotoxic phenotype. Tissue studies revealed an abundance of cells undergoing apoptotic cell death disproportionately involving nonimmune, nonendothelial cells of mesenchymal origin. Apoptotic cells showed significant upregulation of HLA-DR.
Conclusions: CD4+CTLs and CD8+CTLs may induce apoptotic cell death in tissues of patients with IgG4-RD with preferential targeting of nonendothelial, nonimmune cells of mesenchymal origin.
Keywords: CD28(lo); CD28(null); CD4(+)CTL; CD8(+)CTL; IgG(4)-RD; apoptosis.
Copyright © 2020 American Academy of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure statement: The authors have declared that no conflicts of interest exist.
Figures





References
-
- Kamisawa T, Zen Y, Pillai S, Stone JH. IgG4-related disease. Lancet. 2015;385:1460–71. - PubMed
-
- Stone JH, Zen Y, Deshpande V. IgG4-related disease. N Engl J Med. 2012;366:539–51. - PubMed
-
- Wallace ZS, Naden RP, Chari S, Choi HK, Della-Torre E, Dicaire J-F, et al. The 2019 American College of Rheumatology/European League Against Rheumatism classification criteria for IgG4-related disease. Ann Rheum Dis. 2020;79:77–87. - PubMed
-
- Deshpande V, Zen Y, Chan JK, Yi EE, Sato Y, Yoshino T, et al. Consensus statement on the pathology of IgG4-related disease. Mod Pathol. 2012;25:1181–92. - PubMed
-
- Carruthers MN, Topazian MD, Khosroshahi A, Witzig TE, Wallace ZS, Hart PA, et al. Rituximab for IgG4-related disease: a prospective, open-label trial. Ann Rheum Dis. 2015;74:1171–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

