Transcriptional, Epigenetic and Metabolic Programming of Tumor-Associated Macrophages
- PMID: 32486098
- PMCID: PMC7352439
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers12061411
Transcriptional, Epigenetic and Metabolic Programming of Tumor-Associated Macrophages
Abstract
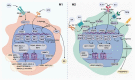
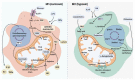
Macrophages are key innate immune cells in the tumor microenvironment (TME) that regulate primary tumor growth, vascularization, metastatic spread and tumor response to various types of therapies. The present review highlights the mechanisms of macrophage programming in tumor microenvironments that act on the transcriptional, epigenetic and metabolic levels. We summarize the latest knowledge on the types of transcriptional factors and epigenetic enzymes that control the direction of macrophage functional polarization and their pro- and anti-tumor activities. We also focus on the major types of metabolic programs of macrophages (glycolysis and fatty acid oxidation), and their interaction with cancer cells and complex TME. We have discussed how the regulation of macrophage polarization on the transcriptional, epigenetic and metabolic levels can be used for the efficient therapeutic manipulation of macrophage functions in cancer.
Keywords: epigenetic regulation; fatty acid oxidation; glycolysis; histones; metabolism; methylation; reprogramming; transcription factors; tumor; tumor-associated macrophages.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Stakheyeva M., Riabov V., Mitrofanova I., Litviakov N., Choynzonov E., Cherdyntseva N., Kzhyshkowska J. Role of the immune component of tumor microenvironment in the efficiency of cancer treatment: Perspectives for the personalized therapy. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2017;23:4807–4826. doi: 10.2174/1381612823666170714161703. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Kzhyshkowska J., Grigoryeva E., Larionova I. Targeting the Tumor-Associated Macrophages for ‘Normalizing’ Cancer. In: Bizzarri M., editor. Approaching Complex. Diseases. Springer; Cham, Switzerland: 2020. pp. 245–274.
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

