Predicting survival in melanoma patients treated with concurrent targeted- or immunotherapy and stereotactic radiotherapy : Melanoma brain metastases prognostic score
- PMID: 32487100
- PMCID: PMC7268472
- DOI: 10.1186/s13014-020-01558-8
Predicting survival in melanoma patients treated with concurrent targeted- or immunotherapy and stereotactic radiotherapy : Melanoma brain metastases prognostic score
Erratum in
-
Correction to: Predicting survival in melanoma patients treated with concurrent targeted- or immunotherapy and stereotactic radiotherapy : Melanoma brain metastases prognostic score.Radiat Oncol. 2020 Dec 14;15(1):280. doi: 10.1186/s13014-020-01708-y. Radiat Oncol. 2020. PMID: 33317582 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Background: Melanoma patients frequently develop brain metastases. The most widely used score to predict survival is the molGPA based on a mixed treatment of stereotactic radiotherapy (SRT) and whole brain radiotherapy (WBRT). In addition, systemic therapy was not considered. We therefore aimed to evaluate the performance of the molGPA score in patients homogeneously treated with SRT and concurrent targeted therapy or immunotherapy (TT/IT).
Methods: This retrospective analysis is based on an international multicenter database (TOaSTT) of melanoma patients treated with TT/IT and concurrent (≤30 days) SRT for brain metastases between May 2011 and May 2018. Overall survival (OS) was studied using Kaplan-Meier survival curves and log-rank testing. Uni- and multivariate analysis was performed to analyze prognostic factors for OS.
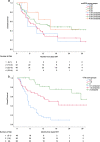
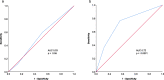
Results: One hundred ten patients were analyzed. 61, 31 and 8% were treated with IT, TT and with a simultaneous combination, respectively. A median of two brain metastases were treated per patient. After a median follow-up of 8 months, median OS was 8.4 months (0-40 months). The molGPA score was not associated with OS. Instead, cumulative brain metastases volume, timing of metastases (syn- vs. metachronous) and systemic therapy with concurrent IT vs. TT influenced OS significantly. Based on these parameters, the VTS score (volume-timing-systemic therapy) was established that stratified patients into three groups with a median OS of 5.1, 18.9 and 34.5 months, respectively (p = 0.001 and 0.03).
Conclusion: The molGPA score was not useful for this cohort of melanoma patients undergoing local therapy for brain metastases taking into account systemic TT/IT. For these patients, we propose a prognostic VTS score, which needs to be validated prospectively.
Keywords: Brain metastases; Immunotherapy; Melanoma; Stereotactic; Targeted therapy; molGPA.
Conflict of interest statement
NS: travel grants from Merck Sharpe & Dohme, Astellas, Bayer and Bristol-Myers-Squibb. DB reports personal fees from Siemens AG, personal fees from NB Capital Research GmbH, personal fees from NB Capital ApS, personal fees from b.e. Imaging GmbH outside the submitted work. MS: remuneration for lectures from Merck Serono and AstraZeneca.
All other authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

