Shock wave lithotripsy, for the treatment of kidney stones, results in changes to routine blood tests and novel biomarkers: a prospective clinical pilot-study
- PMID: 32487191
- PMCID: PMC7268594
- DOI: 10.1186/s40001-020-00417-2
Shock wave lithotripsy, for the treatment of kidney stones, results in changes to routine blood tests and novel biomarkers: a prospective clinical pilot-study
Abstract
Background: The number of patients undergoing shock wave lithotripsy (SWL) for kidney stones is increasing annually, and as such the development of post-operative complications, such as haematuria and acute kidney injury (AKI) following SWL, is likely to increase. The aim of the study was to evaluate changes in routine blood and novel biomarkers following SWL, for the treatment of kidney stones.
Methods: Twelve patients undergoing SWL for solitary unilateral kidney stones were recruited. From patients (8 males and 4 females) aged between 31 and 72 years (median 43 years), venous blood samples were collected pre-operatively (baseline), at 30, 120 and 240 min post-operatively. Routine blood tests were performed using a Sysmex XE-5000, and Beckman Coulter AU5800 and AU680 analysers. NGAL, IL-18, IL-6, TNF-α, IL-10 and IL-8 concentrations were determined using commercially available ELISA kits.
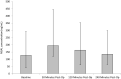
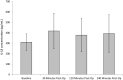
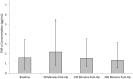
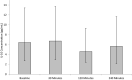
Results: Significant (p ≤ 0.05) changes were observed in several blood parameters following SWL. NGAL concentration significantly increased, with values peaking at 30 min post-treatment (p = 0.033). Although IL-18 concentration increased, these changes were not significant (p = 0.116). IL-6 revealed a statistically significant rise from pre-operative up to 4 h post-operatively (p < 0.001), whilst TNF-α significantly increased, peaking at 30 min post-SWL (p = 0.05). There were no significant changes to IL-10 and IL-8 concentrations post-SWL (p > 0.05).
Conclusions: Changes to routine blood tests and specific biomarkers, in the future, may be more useful for clinicians. In turn, identification of a panel of biomarkers could provide valuable data on "normal" physiological response after lithotripsy. Ultimately, studies could be expanded to identify or predict those patients at increased risk of developing post-operative complications, such as acute kidney injury or. These studies, however, need validating involving larger cohorts.
Keywords: Acute kidney injury (AKI); Biomarkers; Inflammation; Kidney stones; Routine blood tests; Shock wave lithotripsy (SWL).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A Pilot Study to Evaluate Haemostatic Function, following Shock Wave Lithotripsy (SWL) for the Treatment of Solitary Kidney Stones.PLoS One. 2015 May 4;10(5):e0125840. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0125840. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25938233 Free PMC article.
-
Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL) value changes before and after shock wave lithotripsy.Urolithiasis. 2017 Aug;45(4):347-351. doi: 10.1007/s00240-016-0932-3. Epub 2016 Oct 27. Urolithiasis. 2017. PMID: 27787615
-
The role of specific biomarkers, as predictors of post-operative complications following flexible ureterorenoscopy (FURS), for the treatment of kidney stones: a single-centre observational clinical pilot-study in 37 patients.BMC Urol. 2020 Aug 14;20(1):122. doi: 10.1186/s12894-020-00693-4. BMC Urol. 2020. PMID: 32795278 Free PMC article.
-
Endourologic Management (PCNL, URS, SWL) of Stones in Solitary Kidney: A Systematic Review from European Association of Urologists Young Academic Urologists and Uro-Technology Groups.J Endourol. 2020 Jan;34(1):7-17. doi: 10.1089/end.2019.0455. Epub 2019 Sep 26. J Endourol. 2020. PMID: 31456421
-
Lithotripsy.Proc Inst Mech Eng H. 2010;224(2):317-42. doi: 10.1243/09544119JEIM588. Proc Inst Mech Eng H. 2010. PMID: 20349822 Review.
Cited by
-
Current Status of Protein Biomarkers in Urolithiasis-A Review of the Recent Literature.J Clin Med. 2023 Nov 16;12(22):7135. doi: 10.3390/jcm12227135. J Clin Med. 2023. PMID: 38002747 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Selective biomarkers for inflammation and infection are associated with post-operative complications following transperineal template prostate biopsy (TTPB): a single-centre observational clinical pilot-study.Eur J Med Res. 2022 Sep 26;27(1):187. doi: 10.1186/s40001-022-00807-8. Eur J Med Res. 2022. PMID: 36154663 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of Inflammatory Parameters Following Extracorporeal Shock Wave Lithotripsy (ESWL) and Ureteroscopy for the Treatment of Proximal Ureteral Stones.Cureus. 2024 Jan 8;16(1):e51882. doi: 10.7759/cureus.51882. eCollection 2024 Jan. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 38327930 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lee YJ, Oh SN, Rha SE, Byun JY. Renal trauma. Radiol Clin N Am. 2007; 45(3): 581–592, ix. 10.1016/j.rcl.2007.04.004. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

