Multistable and dynamic CRISPRi-based synthetic circuits
- PMID: 32488086
- PMCID: PMC7265303
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-020-16574-1
Multistable and dynamic CRISPRi-based synthetic circuits
Erratum in
-
Author Correction: Multistable and dynamic CRISPRi-based synthetic circuits.Nat Commun. 2021 May 19;12(1):3119. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-23622-x. Nat Commun. 2021. PMID: 34011942 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
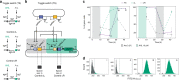
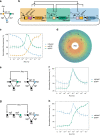
Gene expression control based on CRISPRi (clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats interference) has emerged as a powerful tool for creating synthetic gene circuits, both in prokaryotes and in eukaryotes; yet, its lack of cooperativity has been pointed out as a potential obstacle for dynamic or multistable synthetic circuit construction. Here we use CRISPRi to build a synthetic oscillator ("CRISPRlator"), bistable network (toggle switch) and stripe pattern-forming incoherent feed-forward loop (IFFL). Our circuit designs, conceived to feature high predictability and orthogonality, as well as low metabolic burden and context-dependency, allow us to achieve robust circuit behaviors in Escherichia coli populations. Mathematical modeling suggests that unspecific binding in CRISPRi is essential to establish multistability. Our work demonstrates the wide applicability of CRISPRi in synthetic circuits and paves the way for future efforts towards engineering more complex synthetic networks, boosted by the advantages of CRISPR technology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Synthetic Gene Circuits Combining CRISPR Interference and CRISPR Activation in E. coli: Importance of Equal Guide RNA Binding Affinities to Avoid Context-Dependent Effects.ACS Synth Biol. 2023 Oct 20;12(10):3064-3071. doi: 10.1021/acssynbio.3c00375. Epub 2023 Oct 9. ACS Synth Biol. 2023. PMID: 37813387 Free PMC article.
-
CRISPR-based gene expression control for synthetic gene circuits.Biochem Soc Trans. 2020 Oct 30;48(5):1979-1993. doi: 10.1042/BST20200020. Biochem Soc Trans. 2020. PMID: 32964920 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Overcoming Leak Sensitivity in CRISPRi Circuits Using Antisense RNA Sequestration and Regulatory Feedback.ACS Synth Biol. 2022 Sep 16;11(9):2927-2937. doi: 10.1021/acssynbio.2c00155. Epub 2022 Aug 26. ACS Synth Biol. 2022. PMID: 36017994 Free PMC article.
-
Targeted Transcriptional Repression in Bacteria Using CRISPR Interference (CRISPRi).Methods Mol Biol. 2015;1311:349-62. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-2687-9_23. Methods Mol Biol. 2015. PMID: 25981485 Free PMC article.
-
CRISPR-Cas9/CRISPRi tools for cell factory construction in E. coli.World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2020 Jun 25;36(7):96. doi: 10.1007/s11274-020-02872-9. World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2020. PMID: 32583135 Review.
Cited by
-
Hematopoietic and Chronic Myeloid Leukemia Stem Cells: Multi-Stability versus Lineage Restriction.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Nov 5;23(21):13570. doi: 10.3390/ijms232113570. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36362357 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Synthetic Gene Circuits Combining CRISPR Interference and CRISPR Activation in E. coli: Importance of Equal Guide RNA Binding Affinities to Avoid Context-Dependent Effects.ACS Synth Biol. 2023 Oct 20;12(10):3064-3071. doi: 10.1021/acssynbio.3c00375. Epub 2023 Oct 9. ACS Synth Biol. 2023. PMID: 37813387 Free PMC article.
-
Controlling spatiotemporal pattern formation in a concentration gradient with a synthetic toggle switch.Mol Syst Biol. 2020 Jun;16(6):e9361. doi: 10.15252/msb.20199361. Mol Syst Biol. 2020. PMID: 32529808 Free PMC article.
-
An engineered bacterial symbiont allows noninvasive biosensing of the honey bee gut environment.PLoS Biol. 2024 Mar 5;22(3):e3002523. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.3002523. eCollection 2024 Mar. PLoS Biol. 2024. PMID: 38442124 Free PMC article.
-
Engineering intercellular communication using M13 phagemid and CRISPR-based gene regulation for multicellular computing in Escherichia coli.Nat Commun. 2025 Apr 15;16(1):3569. doi: 10.1038/s41467-025-58760-z. Nat Commun. 2025. PMID: 40234414 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Xie MQ, Fussenegger M. Designing cell function: assembly of synthetic gene circuits for cell biology applications. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2018;19:507–525. - PubMed
-
- Chappell J, Watters KE, Takahashi MK, Lucks JB. A renaissance in RNA synthetic biology: new mechanisms, applications and tools for the future. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2015;28:47–56. - PubMed
-
- Jusiak B, Cleto S, Perez-Pinera P, Lu TK. Engineering synthetic gene circuits in living cells with CRISPR technology. Trends Biotechnol. 2016;34:535–547. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

