Changes of lipoxin levels during pregnancy and the monthly-cycle, condition the normal course of pregnancy or pathology
- PMID: 32488315
- PMCID: PMC7395003
- DOI: 10.1007/s00011-020-01358-6
Changes of lipoxin levels during pregnancy and the monthly-cycle, condition the normal course of pregnancy or pathology
Abstract
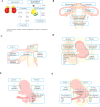
Objective and design: The purpose of the review was to gather information on the role and possibilities of using lipoxin in the treatment of infertility and maintaining a normal pregnancy. Ovulation, menstruation, embryo implantation, and childbirth are reactions representing short-term inflammatory events involving lipoxin activities. Lipoxin A4 (LXA4) is an arachidonic acid metabolite, and in cooperation with its positional isomer lipoxin B4 (LXB4), it is a major lipoxin in mammals. Biosynthesis process occurs in two stages: in the first step, the donor cell releases the eicosanoid intermediate; secondarily, the acceptor cell gets and converts the intermediate product into LXA4 (leukocyte/platelet interaction).
Results: Generating lipoxin synthesis may also be triggered by salicylic acid, which acetylates cyclooxygenase-2. Lipoxin A4 and its analogues are considered as specialized pro-resolving mediators. LXA4 is an important component for a proper menstrual cycle, embryo implantation, pregnancy, and delivery. Its level in the luteal phase is high, while in the follicular phase, it decreases, which coincides with an increase in estradiol concentration with which it competes for the receptor. LXA4 inhibits the progression of endometriosis. However, during the peri-implantation period, before pregnancy is confirmed clinically, high levels of LXA4 can contribute to early pregnancy loss and may cause miscarriage. After implantation, insufficient LXA4 levels contribute to incorrect maternal vessel remodeling; decreased, shallow trophoblastic invasion; and the immuno-energetic abnormality of the placenta, which negatively affects fetal growth and the maintenance of pregnancy. Moreover, the level of LXA4 increases in the final stages of pregnancy, allowing vessel remodeling and placental separation.
Methods: The review evaluates the literature published in the PubMed and Embase database up to 31 December 2019. The passwords were checked on terms: lipoxin and pregnancy with combined endometriosis, menstrual cycle, implantation, pre-eclampsia, fetal growth restriction, and preterm labor.
Conclusions: Although no human studies have been performed so far, the cell and animal model study results suggest that LXA4 will be used in obstetrics and gynecology soon.
Keywords: Inflammation; Lipoxin; Menstruation; Ovulation; Pregnancy; Reproduction.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have not reported any conflict of interest. All authors approved the final version.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Lipoxin A4 and lipoxin B4 stimulate the release but not the oxygenation of arachidonic acid in human neutrophils: dissociation between lipid remodeling and adhesion.J Cell Physiol. 1990 Jun;143(3):512-23. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041430316. J Cell Physiol. 1990. PMID: 2162850
-
Lipoxin A4 blocks embryo implantation by controlling estrogen receptor α activity.Reproduction. 2013 Apr 15;145(4):411-20. doi: 10.1530/REP-12-0469. Print 2013 Apr. Reproduction. 2013. PMID: 23426803
-
Activation of human monocytes and the acute monocytic leukemia cell line (THP-1) by lipoxins involves unique signaling pathways for lipoxin A4 versus lipoxin B4: evidence for differential Ca2+ mobilization.J Immunol. 1996 Sep 1;157(5):2149-54. J Immunol. 1996. PMID: 8757340
-
Lipoxin and synthetic lipoxin analogs: an overview of anti-inflammatory functions and new concepts in immunomodulation.Inflamm Allergy Drug Targets. 2006 Apr;5(2):91-106. doi: 10.2174/187152806776383125. Inflamm Allergy Drug Targets. 2006. PMID: 16613568 Review.
-
The role of lipoxin A4 in endometrial biology and endometriosis.Mucosal Immunol. 2013 May;6(3):439-50. doi: 10.1038/mi.2013.9. Epub 2013 Mar 13. Mucosal Immunol. 2013. PMID: 23485944 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Assessing lipoxin-mediated inflammatory responses in the second trimester of pregnancy among women with obesity: A comprehensive analysis.Turk J Obstet Gynecol. 2023 Dec 8;20(4):255-263. doi: 10.4274/tjod.galenos.2023.16678. Turk J Obstet Gynecol. 2023. PMID: 38073076 Free PMC article.
-
Increased Demand of Obese Women for Protectins, Maresin, and Resolvin D1 in the Last Trimester of Pregnancy.Nutrients. 2023 Oct 11;15(20):4340. doi: 10.3390/nu15204340. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 37892415 Free PMC article.
-
The great obstetrical syndromes and the placenta.BJOG. 2023 Nov;130 Suppl 3(Suppl 3):8-15. doi: 10.1111/1471-0528.17613. Epub 2023 Aug 2. BJOG. 2023. PMID: 37530495 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sex Differences in Otolaryngology: Focus on the Emerging Role of Estrogens in Inflammatory and Pro-Resolving Responses.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Aug 16;22(16):8768. doi: 10.3390/ijms22168768. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34445474 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acid (LC-PUFA) status in severe preeclampsia and preterm birth: a cross sectional study.Sci Rep. 2021 Jul 19;11(1):14701. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-93846-w. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34282168 Free PMC article.
References
-
- von der Weid P-Y, Hollenberg MD, Fiorucci S, Wallace JL. Aspirin-triggered, cyclooxygenase-2–dependent lipoxin synthesis modulates vascular tone. Circulation. 2004;110:1320–1325. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

