One fly-one genome: chromosome-scale genome assembly of a single outbred Drosophila melanogaster
- PMID: 32491177
- PMCID: PMC7367183
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkaa450
One fly-one genome: chromosome-scale genome assembly of a single outbred Drosophila melanogaster
Abstract
A high quality genome assembly is a vital first step for the study of an organism. Recent advances in technology have made the creation of high quality chromosome scale assemblies feasible and low cost. However, the amount of input DNA needed for an assembly project can be a limiting factor for small organisms or precious samples. Here we demonstrate the feasibility of creating a chromosome scale assembly using a hybrid method for a low input sample, a single outbred Drosophila melanogaster. Our approach combines an Illumina shotgun library, Oxford nanopore long reads, and chromosome conformation capture for long range scaffolding. This single fly genome assembly has a N50 of 26 Mb, a length that encompasses entire chromosome arms, contains 95% of expected single copy orthologs, and a nearly complete assembly of this individual's Wolbachia endosymbiont. The methods described here enable the accurate and complete assembly of genomes from small, field collected organisms as well as precious clinical samples.
© The Author(s) 2020. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
Figures
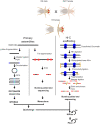
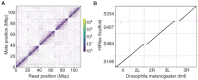
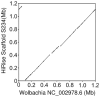
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

