Two hits to the renin-angiotensin system may play a key role in severe COVID-19
- PMID: 32492292
- PMCID: PMC7300771
- DOI: 10.1002/kjm2.12237
Two hits to the renin-angiotensin system may play a key role in severe COVID-19
Abstract
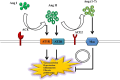
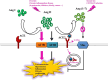
The spike glycoprotein on the virion surface docking onto the angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) 2 dimer is an essential step in the process of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection in human cells-involves downregulation of ACE2 expression with systemic renin-angiotensin system (RAS) imbalance and promotion of multi-organ damage. In general, the RAS induces vasoconstriction, hypertension, inflammation, fibrosis, and proliferation via the ACE/Ang II/Ang II type 1 receptor (AT1R) axis and induces the opposite effects via the ACE2/Ang (1-7)/Mas axis. The RAS may be activated by chronic inflammation in hypertension, diabetes, obesity, and cancer. SARS-CoV-2 induces the ACE2 internalization and shedding, leading to the inactivation of the ACE2/Ang (1-7)/Mas axis. Therefore, we hypothesize that two hits to the RAS drives COVID-19 progression. In brief, the first hit originates from chronic inflammation activating the ACE/Ang II/AT1R axis, and the second originates from the COVID-19 infection inactivating the ACE2/Ang (1-7)/Mas axis. Moreover, the two hits to the RAS may be the primary reason for increased mortality in patients with COVID-19 who have comorbidities and may serve as a therapeutic target for COVID-19 treatment.
Keywords: coronavirus disease 2019; renin-angiotensin system); two hits.
© 2020 The Authors. The Kaohsiung Journal of Medical Sciences published by John Wiley & Sons Australia on behalf of Kaohsiung Medical University.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization (WHO) . Coronavirus disease (COVID‐19) Pandemic [Situation reports]. May 7, 2020. Available from: https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

