Susceptibility of Selected Tea Shoots to Oviposition by Empoasca onukii (Hemiptera: Cicadellidae) and Feasibility of Egg Removal with Harvesting
- PMID: 32492822
- PMCID: PMC7348997
- DOI: 10.3390/insects11060338
Susceptibility of Selected Tea Shoots to Oviposition by Empoasca onukii (Hemiptera: Cicadellidae) and Feasibility of Egg Removal with Harvesting
Abstract
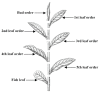
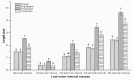
The Empoasca onukii (Hemiptera: Cicadellidae) female lays its eggs inside the epidermis of the tea plant shoots. This has led to speculation that shoot harvesting could represent a method of egg removal. To verify the validity of this hypothesis, we sought to determine which part of the shoot was used for the oviposition and how the value of the harvested shoot affects the cost of the egg removal. In this study, four tea cultivars were chosen to examine the preferences for the site of oviposition. In addition, a mathematical model was used to describe the correlation between the economic value of the selected shoot and eggs laid within the shoot. Our study revealed that the pest preferred the 3rd and 4th leaf order intervals of the shoot as the oviposition sites, and the oviposition preferences was dependent on the leaf order interval class across all tea cultivars. In addition, a significant negative exponential relationship was found between the economic value of the selected shoot and the percentage of the eggs laid within the shoot, indicating that egg removal through shoot harvesting was limited. The findings of this study could be used to better understand the role of shoot harvesting in egg removal and would provide new insights into the understanding of the incidence of this pest.
Keywords: leaf order interval; leafhopper; oviposition preference; pest incidence; shoot characteristics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Saha D., Mukhopadhyay A. Insecticide resistance mechanisms in three sucking insect pests of tea with reference to North-East India: An appraisal. Int. J. Trop. Insect Sci. 2012;33:46–70. doi: 10.1017/S1742758412000380. - DOI
-
- De Costa J., Mohotti A.J., Wijeratne M.A. Ecophysiology of tea. Braz. J. Plant Physiol. 2007;19:299–332. doi: 10.1590/S1677-04202007000400005. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

