Evaluation of Symmetric Dimethylarginine (SDMA) in Dogs with Acute Pancreatitis
- PMID: 32492828
- PMCID: PMC7356378
- DOI: 10.3390/vetsci7020072
Evaluation of Symmetric Dimethylarginine (SDMA) in Dogs with Acute Pancreatitis
Abstract
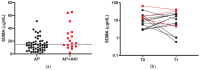
Symmetric dimethylarginine (SDMA) is considered an important biomarker of kidney dysfunction. The aims of the study were to evaluate SDMA in dogs with acute pancreatitis (AP) and its relationship with the presence of kidney injury and mortality. A cohort study including fifty-four dogs with AP diagnosed using compatible clinical and laboratory parameters, abnormal SNAP cPL and compatible abdominal ultrasound within 48 h from admission, was conducted. Dogs with history of renal and/or urinary diseases were excluded, along with dogs exposed to nephrotoxic drugs. Serum urea and creatinine and urinary output (UO) were recorded. Acute kidney injury (AKI) was diagnosed and graded using International Renal Interest Society (IRIS) guidelines. SDMA was measured using high performance liquid chromatography. Fifty-four dogs were included and divided in non-AKI (n = 37) and AKI dogs (n = 17). Twenty-three dogs (14 non-AKI) had SDMA > 15 μg/dL. Median SDMA was higher in AKI dogs than non-AKI dogs (25.7 vs. 13.93 μg/dL; p = 0.03). Dogs with normal creatinine (AP and AKI 1 dogs) had SDMA above reference range in 38% and 33% of cases, respectively. In AKI dogs, SDMA and creatinine were positively correlated (p = 0.006 r = 0.7). SDMA was not significantly different between survivors and non-survivors. Although further studies are warranted, SDMA may be a useful tool in canine AP, as a high SDMA may be related to subclinical kidney impairment.
Keywords: canine; inflammation; kidney injury; pancreas.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

