Long Range Endocrine Delivery of Circulating miR-210 to Endothelium Promotes Pulmonary Hypertension
- PMID: 32493166
- PMCID: PMC7429300
- DOI: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.119.316398
Long Range Endocrine Delivery of Circulating miR-210 to Endothelium Promotes Pulmonary Hypertension
Abstract
Rationale: Unproven theories abound regarding the long-range uptake and endocrine activity of extracellular blood-borne microRNAs into tissue. In pulmonary hypertension (PH), microRNA-210 (miR-210) in pulmonary endothelial cells promotes disease, but its activity as an extracellular molecule is incompletely defined.
Objective: We investigated whether chronic and endogenous endocrine delivery of extracellular miR-210 to pulmonary vascular endothelial cells promotes PH.
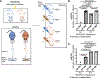
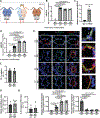
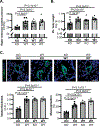
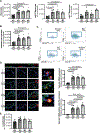
Methods and results: Using miR-210 replete (wild-type [WT]) and knockout mice, we tracked blood-borne miR-210 using bone marrow transplantation and parabiosis (conjoining of circulatory systems). With bone marrow transplantation, circulating miR-210 was derived predominantly from bone marrow. Via parabiosis during chronic hypoxia to induce miR-210 production and PH, miR-210 was undetectable in knockout-knockout mice pairs. However, in plasma and lung endothelium, but not smooth muscle or adventitia, miR-210 was observed in knockout mice of WT-knockout pairs. This was accompanied by downregulation of miR-210 targets ISCU (iron-sulfur assembly proteins)1/2 and COX10 (cytochrome c oxidase assembly protein-10), indicating endothelial import of functional miR-210. Via hemodynamic and histological indices, knockout-knockout pairs were protected from PH, whereas knockout mice in WT-knockout pairs developed PH. In particular, pulmonary vascular engraftment of miR-210-positive interstitial lung macrophages was observed in knockout mice of WT-knockout pairs. To address whether engrafted miR-210-positive myeloid or lymphoid cells contribute to paracrine miR-210 delivery, we studied miR-210 knockout mice parabiosed with miR-210 WT; Cx3cr1 knockout mice (deficient in myeloid recruitment) or miR-210 WT; Rag1 knockout mice (deficient in lymphocytes). In both pairs, miR-210 knockout mice still displayed miR-210 delivery and PH, thus demonstrating a pathogenic endocrine delivery of extracellular miR-210.
Conclusions: Endogenous blood-borne transport of miR-210 into pulmonary vascular endothelial cells promotes PH, offering fundamental insight into the systemic physiology of microRNA activity. These results also describe a platform for RNA-mediated crosstalk in PH, providing an impetus for developing blood-based miR-210 technologies for diagnosis and therapy in this disease.
Keywords: endothelium; lymphocytes; macrophage; microRNAs; parabiosis.
Figures


Comment in
-
Endocrine Delivery of MicroRNA-210: A Trusted Traveler That Mediates Pulmonary Hypertension.Circ Res. 2020 Aug 14;127(5):693-695. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.120.317625. Epub 2020 Aug 13. Circ Res. 2020. PMID: 32790524 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Creemers EE, Tijsen AJ, Pinto YM. Circulating micrornas: Novel biomarkers and extracellular communicators in cardiovascular disease? Circ Res. 2012;110:483–495 - PubMed
-
- He Y, Lin J, Kong D, Huang M, Xu C, Kim TK, Etheridge A, Luo Y, Ding Y, Wang K. Current state of circulating micrornas as cancer biomarkers. Clin Chem. 2015;61:1138–1155 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 HL143967/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL128297/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL122596/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 18EIA33900027/AHA/American Heart Association-American Stroke Association/United States
- R01 HL141080/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 14GRNT19600012/AHA/American Heart Association-American Stroke Association/United States
- R01 HL142629/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL138437/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL140963/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UH3 TR002073/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UH2 TR002073/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL124021/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R00 HL121076/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HL110849/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

