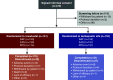
Phase 3, Randomized, Double-Blind, Active-Comparator (Darbepoetin Alfa) Study of Oral Roxadustat in CKD Patients with Anemia on Hemodialysis in Japan
- PMID: 32493693
- PMCID: PMC7350993
- DOI: 10.1681/ASN.2019060623
Phase 3, Randomized, Double-Blind, Active-Comparator (Darbepoetin Alfa) Study of Oral Roxadustat in CKD Patients with Anemia on Hemodialysis in Japan
Abstract
Background: Roxadustat is an oral hypoxia-inducible factor prolyl hydroxylase inhibitor approved in China for dialysis-dependent CKD anemia.
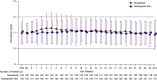
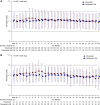
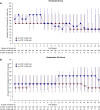
Methods: This phase 3, 24-week, double-blind, double-dummy study evaluated roxadustat's noninferiority to darbepoetin alfa for hemodialysis-dependent CKD anemia. We randomly assigned Japanese patients to oral roxadustat three times weekly or to darbepoetin alfa injections once weekly, titrating doses to maintain hemoglobin between 10-12 g/dl. The primary end point was change of average hemoglobin from baseline to weeks 18-24 (∆Hb18-24). Secondary end points were average hemoglobin and proportion of patients with hemoglobin between 10-12 g/dl (maintenance rate) at weeks 18-24, and iron parameters. Safety assessments included treatment-emergent adverse events and adjudicated ophthalmologic findings.
Results: We randomly assigned 303 patients to roxadustat (n=151) or darbepoetin alfa (n=152). The difference between roxadustat and darbepoetin alfa in ∆Hb18-24 was -0.02 g/dl (95% confidence interval, -0.18 to 0.15), confirming roxadustat's noninferiority to darbepoetin alfa. Average hemoglobin at weeks 18-24 with roxadustat was 10.99 g/dl (95% confidence interval: 10.88 to 11.10), confirming its efficacy. Among patients with one or more hemoglobin value during weeks 18-24, the maintenance rate was 95.2% with roxadustat and 91.3% with darbepoetin alfa. Serum iron, ferritin, and transferrin saturation remained clinically stable with roxadustat; transferrin and total iron binding capacity increased through week 4 before stabilizing. Common treatment-emergent adverse events were nasopharyngitis, shunt stenosis, diarrhea, contusion, and vomiting. The proportion of patients with new or worsening retinal hemorrhage was 32.4% with roxadustat and 36.6% with darbepoetin alfa. We observed no clinically meaningful changes in retinal thickness groups.
Conclusions: Roxadustat maintained hemoglobin within 10-12 g/dl in patients on hemodialysis and was noninferior to darbepoetin alfa. Treatment-emergent adverse events were consistent with previous reports.
Clinical trial registry name and registration number: A Study of Intermittent Oral Dosing of ASP1517 in Hemodialysis Chronic Kidney Disease Patients with Anemia, NCT02952092 (ClinicalTrials.gov).
Keywords: anemia; chronic kidney disease; clinical trial; darbepoetin alfa; hemodialysis; roxadustat.
Copyright © 2020 by the American Society of Nephrology.
Figures
Comment in
-
Role of Roxadustat for ESA-Resistant Renal Anemia? -Read with Caution.J Am Soc Nephrol. 2020 Nov;31(11):2737. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2020060821. Epub 2020 Sep 4. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2020. PMID: 32897870 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Authors' Reply.J Am Soc Nephrol. 2020 Nov;31(11):2738-2740. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2020071096. Epub 2020 Sep 4. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2020. PMID: 32915765 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Authors' Reply.J Am Soc Nephrol. 2021 Apr;32(4):1005-1007. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2021010051. Epub 2021 Mar 1. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2021. PMID: 33649099 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Roxadustat for Renal Anemia in ESRD from PKD Patients: Is It Safe Enough?J Am Soc Nephrol. 2021 Apr;32(4):1005. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2020111664. Epub 2021 Mar 1. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2021. PMID: 33649100 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Del Vecchio L, Locatelli F: An overview on safety issues related to erythropoiesis-stimulating agents for the treatment of anaemia in patients with chronic kidney disease. Expert Opin Drug Saf 15: 1021–1030, 2016. - PubMed
-
- Akizawa T, Okumura H, Alexandre AF, Fukushima A, Kiyabu G, Dorey J: Burden of anemia in chronic kidney disease patients in japan: A literature review. Ther Apher Dial 22: 444–456, 2018. - PubMed
-
- Johnson DW, Pollock CA, Macdougall IC: Erythropoiesis-stimulating agent hyporesponsiveness. Nephrology (Carlton) 12: 321–330, 2007. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

