The Basic Leucine Zipper Transcription Factor PlBZP32 Associated with the Oxidative Stress Response Is Critical for Pathogenicity of the Lychee Downy Blight Oomycete Peronophythora litchii
- PMID: 32493721
- PMCID: PMC7273347
- DOI: 10.1128/mSphere.00261-20
The Basic Leucine Zipper Transcription Factor PlBZP32 Associated with the Oxidative Stress Response Is Critical for Pathogenicity of the Lychee Downy Blight Oomycete Peronophythora litchii
Abstract
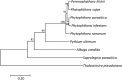
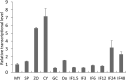
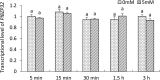
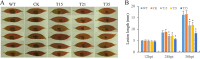
Basic leucine zipper (bZIP) transcription factors are widespread in eukaryotes, including plants, animals, fungi, and oomycetes. However, the functions of bZIPs in oomycetes are rarely known. In this study, we identified a bZIP protein possessing a special bZIP-PAS structure in Peronophythora litchii, named PlBZP32 We found that PlBZP32 is upregulated in zoospores, in cysts, and during invasive hyphal growth. We studied the functions of PlBZP32 using the RNAi technique to suppress the expression of this gene. PlBZP32-silenced mutants were more sensitive to oxidative stress, showed a lower cyst germination rate, and produced more sporangia than the wild-type strain SHS3. The PlBZP32-silenced mutants were also less invasive on the host plant. Furthermore, we analyzed the activities of extracellular peroxidases and laccases and found that silencing PlBZP32 decreased the activities of P. litchii peroxidase and laccase. To our knowledge, this is the first report that the functions of a bZIP-PAS protein are associated with oxidative stress, asexual development, and pathogenicity in oomycetes.IMPORTANCE In this study, we utilized the RNAi technique to investigate the functions of PlBZP32, which possesses a basic leucine zipper (bZIP)-PAS structure, and provided insights into the contributions of bZIP transcription factors to oxidative stress, the production of sporangia, the germination of cysts, and the pathogenicity of Peronophythora litchii This study also revealed the role of PlBZP32 in regulating the enzymatic activities of extracellular peroxidases and laccases in the plant-pathogenic oomycete.
Keywords: Peronophythora litchii; bZIP transcription factor; laccase; pathogenicity; peroxidase.
Copyright © 2020 Kong et al.
Figures




Similar articles
-
The Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase PlMAPK2 Is Involved in Zoosporogenesis and Pathogenicity of Peronophythoralitchii.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Mar 29;22(7):3524. doi: 10.3390/ijms22073524. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33805371 Free PMC article.
-
A Puf RNA-binding protein encoding gene PlM90 regulates the sexual and asexual life stages of the litchi downy blight pathogen Peronophythora litchii.Fungal Genet Biol. 2017 Jan;98:39-45. doi: 10.1016/j.fgb.2016.12.002. Epub 2016 Dec 7. Fungal Genet Biol. 2017. PMID: 27939344
-
Autophagy-Related Gene PlATG6a Is Involved in Mycelial Growth, Asexual Reproduction and Tolerance to Salt and Oxidative Stresses in Peronophythora litchii.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Feb 6;23(3):1839. doi: 10.3390/ijms23031839. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35163762 Free PMC article.
-
Basic leucine zipper domain transcription factors: the vanguards in plant immunity.Biotechnol Lett. 2017 Dec;39(12):1779-1791. doi: 10.1007/s10529-017-2431-1. Epub 2017 Sep 6. Biotechnol Lett. 2017. PMID: 28879532 Review.
-
Basic leucine zipper (bZIP) transcription factors involved in abiotic stresses: A molecular model of a wheat bZIP factor and implications of its structure in function.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016 Jan;1860(1 Pt A):46-56. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagen.2015.10.014. Epub 2015 Oct 20. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016. PMID: 26493723 Review.
Cited by
-
Phase-specific transcriptional patterns of the oomycete pathogen Phytophthora sojae unravel genes essential for asexual development and pathogenic processes.PLoS Pathog. 2023 Mar 23;19(3):e1011256. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1011256. eCollection 2023 Mar. PLoS Pathog. 2023. PMID: 36952577 Free PMC article.
-
A New Insight into 6-Pentyl-2H-pyran-2-one against Peronophythora litchii via TOR Pathway.J Fungi (Basel). 2023 Aug 21;9(8):863. doi: 10.3390/jof9080863. J Fungi (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37623635 Free PMC article.
-
The Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase PlMAPK2 Is Involved in Zoosporogenesis and Pathogenicity of Peronophythoralitchii.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Mar 29;22(7):3524. doi: 10.3390/ijms22073524. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33805371 Free PMC article.
-
Signal and regulatory mechanisms involved in spore development of Phytophthora and Peronophythora.Front Microbiol. 2022 Sep 9;13:984672. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.984672. eCollection 2022. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 36160220 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A C2H2 Zinc Finger Protein PlCZF1 Is Necessary for Oospore Development and Virulence in Peronophythora litchii.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Mar 1;23(5):2733. doi: 10.3390/ijms23052733. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35269874 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Jiang YM, Wang Y, Song L, Liu H, Lichter A, Kerdchoechuen O, Joyce DC, Shi J. 2006. Postharvest characteristics and handling of litchi fruit—an overview. Aust J Exp Agric 46:1541–1556. doi:10.1071/EA05108. - DOI
-
- Qi W, Chen H, Luo T, Song F. 2019. Development status, trend and suggestion of litchi industry in mainland China. Guangdong Nong Ye Ke Xue 46:132–139.
-
- Kao C, Leu L. 1980. Sporangium germination of Peronophythora litchii, the causal organism of litchi downy blight. Mycologia 72:737–748. doi:10.1080/00275514.1980.12021242. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
