Impact of hypoxia on chemoresistance of mesothelioma mediated by the proton-coupled folate transporter, and preclinical activity of new anti-LDH-A compounds
- PMID: 32493992
- PMCID: PMC7434895
- DOI: 10.1038/s41416-020-0912-9
Impact of hypoxia on chemoresistance of mesothelioma mediated by the proton-coupled folate transporter, and preclinical activity of new anti-LDH-A compounds
Abstract
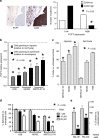
Background: Expression of proton-coupled folate transporter (PCFT) is associated with survival of mesothelioma patients treated with pemetrexed, and is reduced by hypoxia, prompting studies to elucidate their correlation.
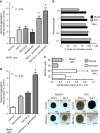
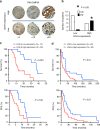
Methods: Modulation of glycolytic gene expression was evaluated by PCR arrays in tumour cells and primary cultures growing under hypoxia, in spheroids and after PCFT silencing. Inhibitors of lactate dehydrogenase (LDH-A) were tested in vitro and in vivo. LDH-A expression was determined in tissue microarrays of radically resected malignant pleural mesothelioma (MPM, N = 33) and diffuse peritoneal mesothelioma (DMPM, N = 56) patients.
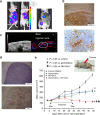
Results: Overexpression of hypoxia marker CAIX was associated with low PCFT expression and decreased MPM cell growth inhibition by pemetrexed. Through integration of PCR arrays in hypoxic cells and spheroids and following PCFT silencing, we identified the upregulation of LDH-A, which correlated with shorter survival of MPM and DMPM patients. Novel LDH-A inhibitors enhanced spheroid disintegration and displayed synergistic effects with pemetrexed in MPM and gemcitabine in DMPM cells. Studies with bioluminescent hypoxic orthotopic and subcutaneous DMPM athymic-mice models revealed the marked antitumour activity of the LDH-A inhibitor NHI-Glc-2, alone or combined with gemcitabine.
Conclusions: This study provides novel insights into hypoxia/PCFT-dependent chemoresistance, unravelling the potential prognostic value of LDH-A, and demonstrating the preclinical activity of LDH-A inhibitors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Vogelzang NJ, Rusthoven JJ, Symanowski J, Denham C, Kaukel E, Ruffie P, et al. Phase III study of pemetrexed in combination with cisplatin versus cisplatin alone in patients with malignant pleural mesothelioma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2003;21:2636–2644. - PubMed
-
- Ceresoli GL, Zucali PA, Favaretto AG, Grossi F, Bidoli P, Del Conte G, et al. Phase II study of pemetrexed plus carboplatin in malignant pleural mesothelioma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2006;24:1443–1448. - PubMed
-
- Righi L, Papotti MG, Ceppi P, Billè A, Bacillo E, Molinaro L, et al. Thymidylate synthase but not excision repair cross-complementation group 1 tumor expression predicts outcome in patients with malignant pleural mesothelioma treated with pemetrexed-based chemotherapy. J. Clin. Oncol. 2010;28:1534–1539. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

