CX3CL1 homo-oligomerization drives cell-to-cell adherence
- PMID: 32494000
- PMCID: PMC7271195
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-020-65988-w
CX3CL1 homo-oligomerization drives cell-to-cell adherence
Abstract
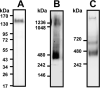
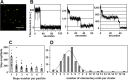
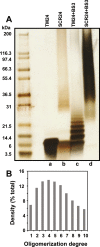
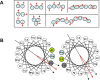
During inflammatory response, blood leukocytes adhere to the endothelium. This process involves numerous adhesion molecules, including a transmembrane chemokine, CX3CL1, which behaves as a molecular cluster. How this cluster assembles and whether this association has a functional role remain unknown. The analysis of CX3CL1 clusters using native electrophoresis and single molecule fluorescence kinetics shows that CX3CL1 is a homo-oligomer of 3 to 7 monomers. Fluorescence recovery after photobleaching assays reveal that the CX3CL1-transmembrane domain peptide self-associates in both cellular and acellular lipid environments, while its random counterpart (i.e. peptide with the same residues in a different order) does not. This strongly indicates that CX3CL1 oligomerization is driven by its intrinsic properties. According to the molecular modeling, CX3CL1 does not associate in compact bundles but rather with monomers linearly assembled side by side. Finally, the CX3CL1 transmembrane peptide inhibits both the CX3CL1 oligomerization and the adhesive function, while its random counterpart does not. This demonstrates that CX3CL1 oligomerization is mandatory for its adhesive potency. Our results provide a new direction to control CX3CL1-dependent cellular adherence in key immune processes.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors E.M.D. and A.J. are employees of CALIXAR that have patents applications that cover CALX173ACE described in this manuscript. Apart from that, the authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Luster, A. D., Alon, R. & von Andrian, U. H. Immune cell migration in inflammation: present and future therapeutic targets. Nat Immunol6, 1182–1190, doi:10.1038/ni1275 (2005). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

