Labeled oxytocin administered via the intranasal route reaches the brain in rhesus macaques
- PMID: 32494001
- PMCID: PMC7270110
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-020-15942-1
Labeled oxytocin administered via the intranasal route reaches the brain in rhesus macaques
Abstract
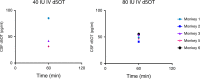
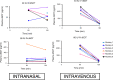
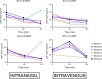
Oxytocin may have promise as a treatment for neuropsychiatric disorders. Its therapeutic effect may depend on its ability to enter the brain and bind to the oxytocin receptor. To date, the brain tissue penetrance of intranasal oxytocin has not been demonstrated. In this nonhuman primate study, we administer deuterated oxytocin intranasally and intravenously to rhesus macaques and measure, with mass spectrometry, concentrations of labeled (exogenously administered) and endogenous oxytocin in 12 brain regions two hours after oxytocin administration. Labeled oxytocin is quantified after intranasal (not intravenous) administration in brain regions (orbitofrontal cortex, striatum, brainstem, and thalamus) that lie in the trajectories of the olfactory and trigeminal nerves. These results suggest that intranasal administration bypasses the blood-brain barrier, delivering oxytocin to specific brain regions, such as the striatum, where oxytocin acts to impact motivated behaviors. Further, high concentrations of endogenous oxytocin are in regions that overlap with projection fields of oxytocinergic neurons.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

