Vascular Calcification: An Important Understanding in Nephrology
- PMID: 32494148
- PMCID: PMC7229867
- DOI: 10.2147/VHRM.S242685
Vascular Calcification: An Important Understanding in Nephrology
Abstract
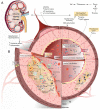
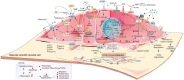
Vascular calcification (VC) is a life-threatening state in chronic kidney disease (CKD). High cardiovascular mortality and morbidity of CKD cases may root from medial VC promoted by hyperphosphatemia. Vascular calcification is an active, highly regulated, and complex biological process that is mediated by genetics, epigenetics, dysregulated form of matrix mineral metabolism, hormones, and the activation of cellular signaling pathways. Moreover, gut microbiome as a source of uremic toxins (eg, phosphate, advanced glycation end products and indoxyl-sulfate) can be regarded as a potential contributor to VC in CKD. Here, an update on different cellular and molecular processes involved in VC in CKD is discussed to elucidate the probable therapeutic pathways in the future.
Keywords: CKD; calcification; chronic kidney disease; hyperphosphatemia; uremia; uremic toxins.
© 2020 Zununi Vahed et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest regarding this work.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

