Efficacy of a Dermocosmetic Serum Combining Bakuchiol and Vanilla Tahitensis Extract to Prevent Skin Photoaging in vitro and to Improve Clinical Outcomes for Naturally Aged Skin
- PMID: 32494181
- PMCID: PMC7231787
- DOI: 10.2147/CCID.S235880
Efficacy of a Dermocosmetic Serum Combining Bakuchiol and Vanilla Tahitensis Extract to Prevent Skin Photoaging in vitro and to Improve Clinical Outcomes for Naturally Aged Skin
Abstract
Background: Skin aging is characterized by slacking and loss of density, especially under ultraviolet (UV) radiation exposure.
Objective: To investigate the beneficial effects of a combination containing bakuchiol (BK) and vanilla tahitensis extract (VTE) to prevent skin photoaging in vitro and to improve clinical outcomes for naturally aged skin.
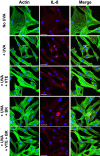
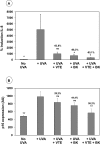
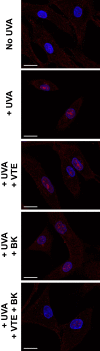
Materials and methods: Human dermal fibroblasts were treated with active compounds, exposed to an acute dose of UVA and analyzed by confocal microscopy: actin network for morphology, interleukin-8 (IL-8) for inflammation and p16 for senescence. Human skin was used to evaluate chronic UVA-induced glycosaminoglycan (GAG) loss and to assess the benefit of topical application of a BK+VTE serum (Alcian blue staining). An open-label clinical trial was conducted in women applying the serum twice daily for 56 days (n=43). Skin remodeling was assessed by FaceScan®. Firmness was evaluated through Dynaskin® and clinical scoring. Skin radiance was also rated on standardized full-face photographs.
Results: UVA induced a significant increase in IL-8 and p16 expression and marked morphological changes in fibroblasts. Treatment with BK or VTE alone prevented both actin network alteration and IL-8 upregulation. Interestingly, BK+VTE demonstrated synergistic protection against IL-8 and p16 overexpression. Serum application prevented GAG loss at the dermo-epidermal junction and increased dermal GAG in UVA-exposed skin explants. In the clinical trial, face ptosis was reduced by 11% on average for 26 responsive subjects and up to 23%. Depth of skin deformation was also reduced by 24% on average for 30 responsive subjects and up to 30%. This firming effect was confirmed by clinical scoring. Radiance was significantly improved by 29% on average for 33 responsive subjects. The serum demonstrated good tolerance/safety.
Conclusion: BK+VTE combination demonstrated anti-aging efficacy and might provide a substantial benefit in the daily care of naturally aged skin in women, through their synergistic effect on inflammaging and senescence.
Keywords: anti-aging therapy; clinical trial; inflammaging; senescence; skin model.
© 2020 Bacqueville et al.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors are employees of Pierre Fabre group, France. The authors report no other conflicts of interest associated with this work.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Epidermal and Dermal Hallmarks of Photoaging are Prevented by Treatment with Night Serum Containing Melatonin, Bakuchiol, and Ascorbyl Tetraisopalmitate: In Vitro and Ex Vivo Studies.Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2020 Feb;10(1):191-202. doi: 10.1007/s13555-019-00349-8. Epub 2020 Jan 3. Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2020. PMID: 31900804 Free PMC article.
-
Sunscreens containing the broad-spectrum UVA absorber, Mexoryl SX, prevent the cutaneous detrimental effects of UV exposure: a review of clinical study results.Photodermatol Photoimmunol Photomed. 2008 Aug;24(4):164-74. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0781.2008.00365.x. Photodermatol Photoimmunol Photomed. 2008. PMID: 18717957 Review.
-
Effects of baicalin against UVA-induced photoaging in skin fibroblasts.Am J Chin Med. 2014;42(3):709-27. doi: 10.1142/S0192415X14500463. Am J Chin Med. 2014. PMID: 24871661
-
A new dermocosmetic containing retinaldehyde, delta-tocopherol glucoside and glycylglycine oleamide for managing naturally aged skin: results from in vitro to clinical studies.Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2017 Feb 2;10:35-42. doi: 10.2147/CCID.S123575. eCollection 2017. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2017. PMID: 28203099 Free PMC article.
-
Broad-spectrum sunscreens provide better protection from solar ultraviolet-simulated radiation and natural sunlight-induced immunosuppression in human beings.J Am Acad Dermatol. 2008 May;58(5 Suppl 2):S149-54. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2007.04.035. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2008. PMID: 18410801 Review.
Cited by
-
Bakuchiol - a natural meroterpenoid: structure, isolation, synthesis and functionalization approaches.RSC Adv. 2022 Mar 21;12(14):8815-8832. doi: 10.1039/d1ra08771a. eCollection 2022 Mar 15. RSC Adv. 2022. PMID: 35424800 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cosmeceuticals for antiaging: a systematic review of safety and efficacy.Arch Dermatol Res. 2024 May 17;316(5):173. doi: 10.1007/s00403-024-02908-2. Arch Dermatol Res. 2024. PMID: 38758222
-
Repurposing INCI-registered compounds as skin prebiotics for probiotic Staphylococcus epidermidis against UV-B.Sci Rep. 2020 Dec 9;10(1):21585. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-78132-5. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 33299009 Free PMC article.
-
Inflammaging and Immunosenescence as Part of Skin Aging-A Narrative Review.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Apr 24;24(9):7784. doi: 10.3390/ijms24097784. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37175491 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Natural Retinol Analogs Potentiate the Effects of Retinal on Aged and Photodamaged Skin: Results from In Vitro to Clinical Studies.Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2023 Oct;13(10):2299-2317. doi: 10.1007/s13555-023-01004-z. Epub 2023 Aug 24. Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2023. PMID: 37615835 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Uitto J. The role of elastin and collagen in cutaneous aging: intrinsic aging versus photoexposure. J Drugs Dermatol. 2008;7(2 Suppl):s12–s16. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

