Nanovesicles derived from iron oxide nanoparticles-incorporated mesenchymal stem cells for cardiac repair
- PMID: 32494669
- PMCID: PMC7195131
- DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.aaz0952
Nanovesicles derived from iron oxide nanoparticles-incorporated mesenchymal stem cells for cardiac repair
Abstract
Because of poor engraftment and safety concerns regarding mesenchymal stem cell (MSC) therapy, MSC-derived exosomes have emerged as an alternative cell-free therapy for myocardial infarction (MI). However, the diffusion of exosomes out of the infarcted heart following injection and the low productivity limit the potential of clinical applications. Here, we developed exosome-mimetic extracellular nanovesicles (NVs) derived from iron oxide nanoparticles (IONPs)-incorporated MSCs (IONP-MSCs). The retention of injected IONP-MSC-derived NVs (IONP-NVs) within the infarcted heart was markedly augmented by magnetic guidance. Furthermore, IONPs significantly increased the levels of therapeutic molecules in IONP-MSCs and IONP-NVs, which can reduce the concern of low exosome productivity. The injection of IONP-NVs into the infarcted heart and magnetic guidance induced an early shift from the inflammation phase to the reparative phase, reduced apoptosis and fibrosis, and enhanced angiogenesis and cardiac function recovery. This approach can enhance the therapeutic potency of an MSC-derived NV therapy.
Copyright © 2020 The Authors, some rights reserved; exclusive licensee American Association for the Advancement of Science. No claim to original U.S. Government Works. Distributed under a Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial License 4.0 (CC BY-NC).
Figures
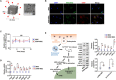



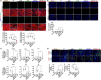

References
-
- Gaziano T. A., Cardiovascular disease in the developing world and its cost-effective management. Circulation 112, 3547–3553 (2005). - PubMed
-
- Writing Group Members, Mozaffarian D., Benjamin E. J., Go A. S., Arnett D. K., Blaha M. J., Cushman M., Das S. R., de Ferranti S., Després J. P., Fullerton H. J., Howard V. J., Huffman M. D., Isasi C. R., Jiménez M. C., Judd S. E., Kissela B. M., Lichtman J. H., Lisabeth L. D., Liu S., Mackey R. H., Magid D. J., McGuire D. K., Mohler E. R. III, Moy C. S., Muntner P., Mussolino M. E., Nasir K., Neumar R. W., Nichol G., Palaniappan L., Pandey D. K., Reeves M. J., Rodriguez C. J., Rosamond W., Sorlie P. D., Stein J., Towfighi A., Turan T. N., Virani S. S., Woo D., Yeh R. W.; American Heart Association Statistics Committee; Stroke Statistics Subcommittee , Heart disease and stroke statistics-2016 update: A report from the american heart association. Circulation 133, E38–E360 (2016). - PubMed
-
- Amado L. C., Saliaris A. P., Schuleri K. H., St John M., Xie J. S., Cattaneo S., Durand D. J., Fitton T., Kuang J. Q., Stewart G., Lehrke S., Baumgartner W. W., Martin B. J., Heldman A. W., Hare J. M., Cardiac repair with intramyocardial injection of allogeneic mesenchymal stem cells after myocardial infarction. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 102, 11474–11479 (2005). - PMC - PubMed
-
- Shake J. G., Gruber P. J., Baumgartner W. A., Senechal G., Meyers J., Redmond J. M., Pittenger M. F., Martin B. J., Mesenchymal stem cell implantation in a swine myocardial infarct model: Engraftment and functional effects. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 73, 1919–1925 (2002). - PubMed
-
- Delewi R., Andriessen A., Tijssen J. G. P., Zijlstra F., Piek J. J., Hirsch A., Impact of intracoronary cell therapy on left ventricular function in the setting of acute myocardial infarction: A meta-analysis of randomised controlled clinical trials. Heart 99, 225–232 (2013). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

